Figure 4.
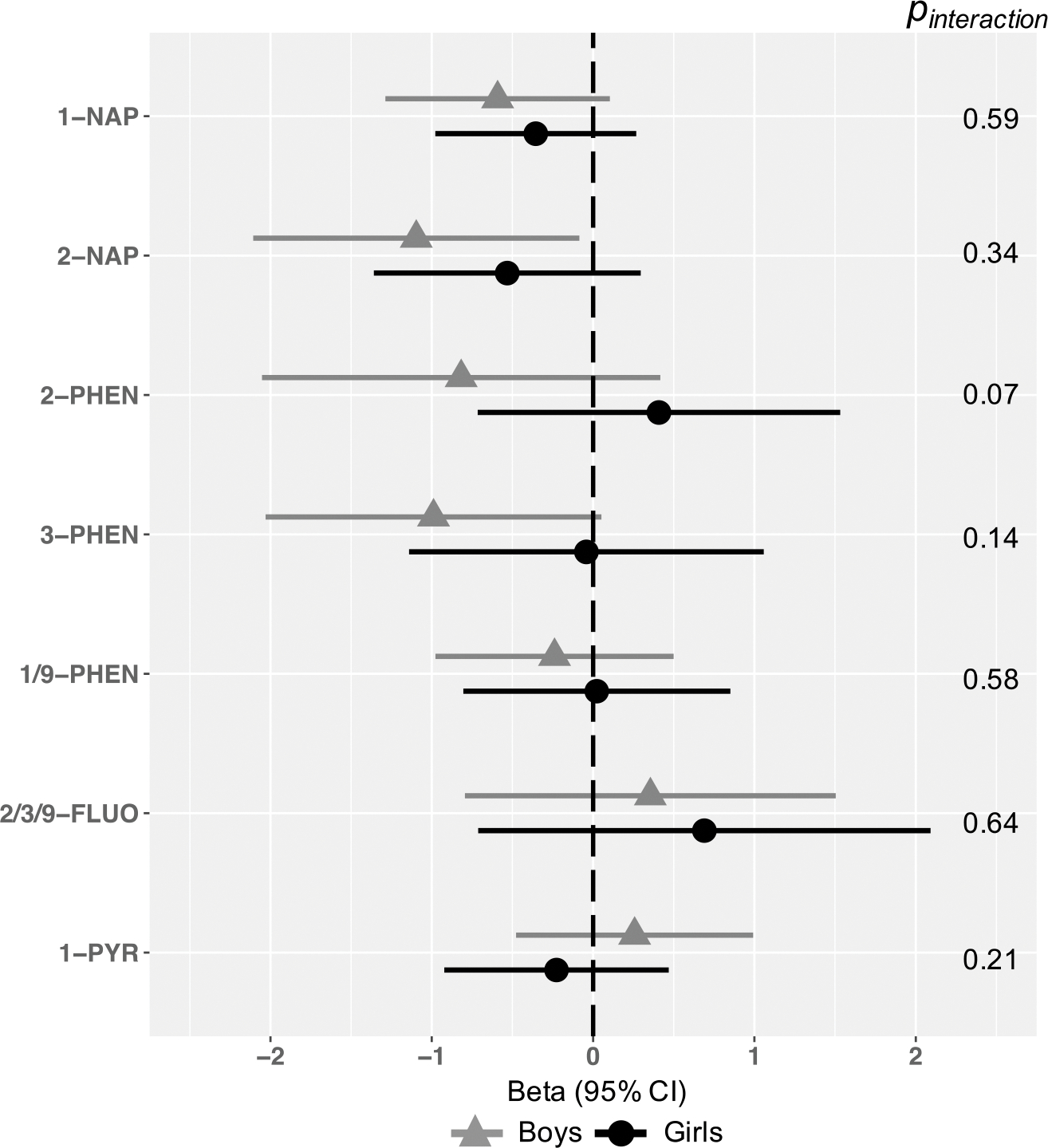
Associations between OH-PAH metabolites and age 4–6 Total Problems, by child sex.
Models represent effect estimates (symbols) and 95% confidence intervals (bars) from linear regressions. Adjusted for child age at assessment (continuous year, to two decimal places), child sex (binary), CBCL form version (binary), OH-PAH analysis batch, and urinary specific gravity (continuous). maternal education (categorical), adjusted income by household count (continuous, natural log transformed), household count (categorical), interaction between adjusted income by family household size (i.e. log income X household count), maternal age at child’s birth (continuous), marital status (married or living with partner vs. not), child birth order (binary, first born vs. not), study site (categorical, 7, with Seattle GAPPS and Seattle TIDES modeled separately), maternal depression (PROMIS score, continuous), maternal stress (Perceived Stress scale, continuous), Child Opportunity Index Social and Economic domain (continuous), Child Opportunity Index Education, pre- and post-natal secondhand smoke exposure (self-reported; any vs. none), and postnatal maternal smoking (self-reported; any vs. none). All estimates represent effect per 2-fold increase in log OH-PAH.
Abbreviations: 1-NAP= 1-hydroxynaphthalene, 2-NAP=2-hydroxynaphthalene, 2-PHEN=2-hydroxyphenanthrene, 3-PHEN=3-hydroxyphenanthrene, 1/9-PHEN=1/9-hydroxyphenanthrene, 2/3/9-FLUO=2/3/9-hydroxyfluorene, 1-PYR=1-hydroxypyrene, 95% CI = 95% Confidence Interval.
