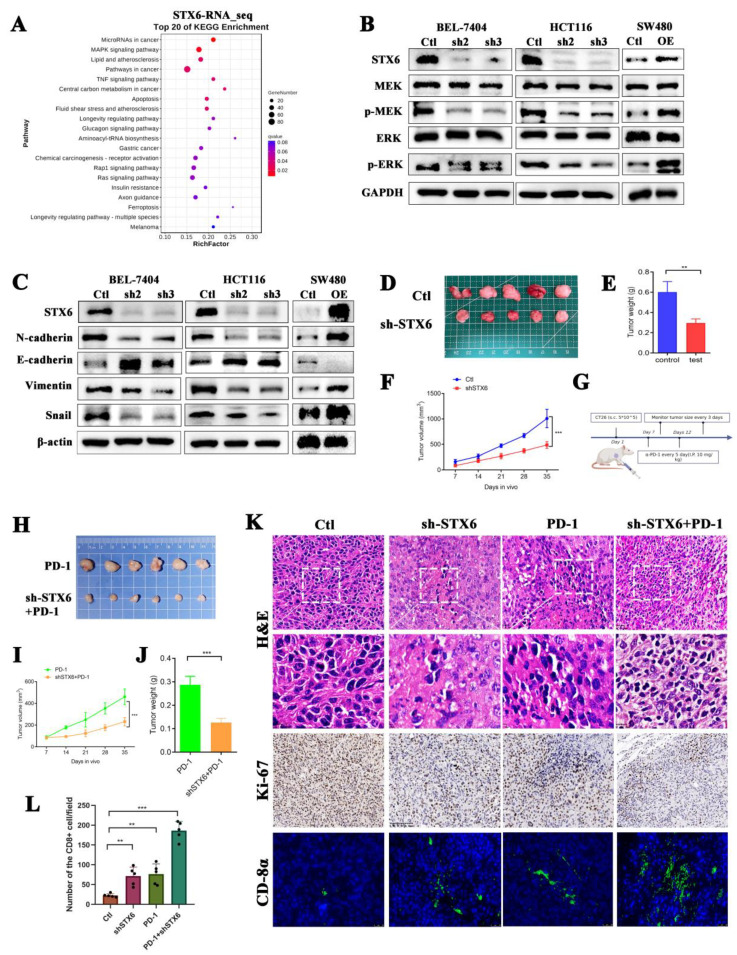
Figure 8.
Knockdown of STX6 expression inhibited tumor formation and promoted CD8 cell infiltration in a mouse model. The RNA-seq results about the knockdown of STX6 in BEL-7404 cells showed that STX6 is involved in cancer pathways, microRNA cancer pathways, and MAPK signaling pathways (A). Knocking down STX6 levels arrested the MAPK/ERK pathway and EMT pathway in HCC and CRC cells, while overexpression of STX6 promoted the activities of the above two pathways (B,C). Tumor weight and volume decreased when they were formed subcutaneously by injection of CT26 cells with silencing of STX6 (D–F). Schematic diagram of CT26 subcutaneous tumorigenesis and anti-PD-1 therapy plan (G). Silencing the STX6 level potentiated the anti-PD-1 efficacy in the mouse model (H–J). The immunofluorescent test (immunohistochemistry) showed that the scores of tumor proliferation-related indices in the STX6 knockdown group or STX6 knockdown combined with anti-PD-1 therapy were lower than those in the control group or anti-PD-1 therapy respectively and promoted CD8 cell infiltration in the mouse model (K,L). ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. The whole Western Blot can be found in file S2.