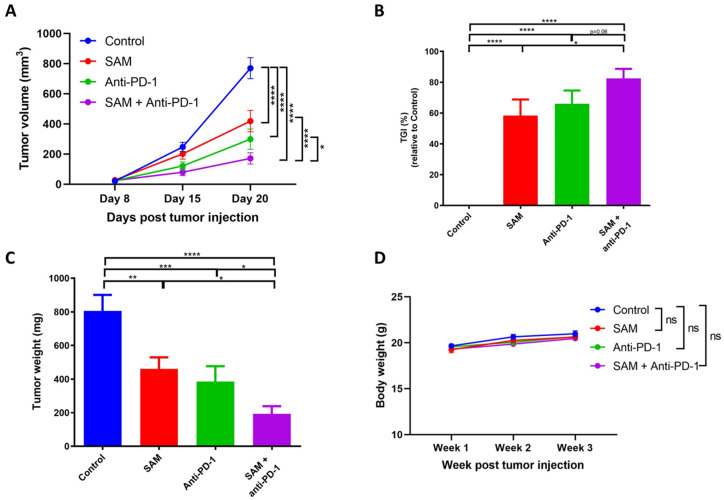
Figure 3.
SAM, anti-PD-1 antibody, and the combination treatment decreased primary tumor growth in Eo771 tumor-bearing mice. (A) Eo771 (2 × 105 cells) were injected at the 4th m.f.p in B6 mice to induce tumor formation. The animals were treated with either the control (isotype matched IgG and PBS), SAM (80 mg/kg/day), anti-PD-1 antibody (5 mg/kg, twice per week), or combination. Tumor volumes were assessed at day 8, 15, and 20, and the animals were sacrificed at day 20. Results are presented as the mean ± SEM of tumor volume (n ≥ 7/group). (B) Percentage tumor growth inhibition (TGI) was calculated from tumor volumes at day 15 to day 20, relative to the control. (C) Tumor weight (mg ± SEM) was measured after tumor harvest on day 20. (D) Body weight (g ± SEM) of the mice was measured once a week. Statistical significance was determined by (A, D) two-way ANOVA; (B, C) one-way ANOVA in GraphPad prism. Significance values are represented by asterisks (ns, not significant; * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001 and **** p < 0.0001).