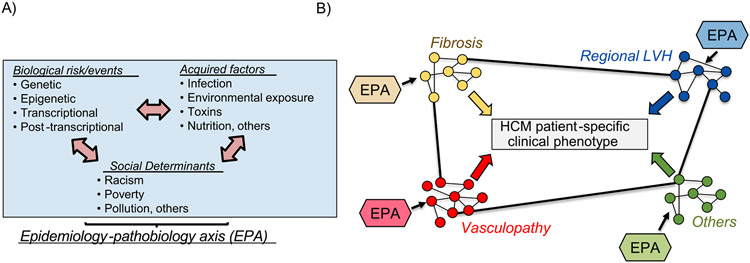
Figure 2.
HCM is a disease of converging endophenotypes, regulated by complex interaction between genetic, post-transcriptional, and environmental determinants. (A) Genetic, biological, acquired, and social profiles likely influence individual functional protein-protein interaction patterns in individual patients with HCM. (B) This paradigm sets the framework for a model that integrates genetic context with environmental determinants of disease to explain HCM. Cross-talk among PPIs between endophenotypes, which may vary between patients, explains heterogeneity in clinical phenotypes evident in HCM populations. EPA = epidemiologic-pathological axis.