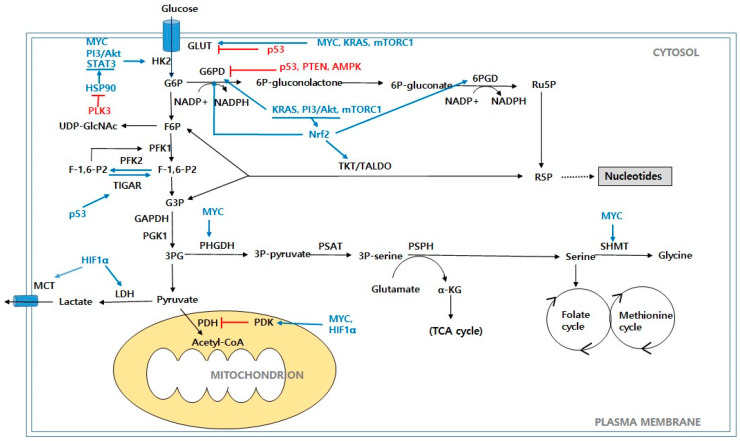
Figure 1.
Glucose metabolism in cancer cells. Schematic representation of main metabolic pathways that contribute to production of biomass precursors, including glycolysis, PPP, HBP, and serine biosynthesis pathway. Abbreviations: GLUT: glucose transporter; HK2: hexokinase 2; G6P: glucose-6-phosphate; F6P: fructose-6-phosphate; PFK1: phosphofructokinase 1; PFK2: phosphofructokinase 2; F-1,6-P2: fructose-1,6-biphosphate; F-2,6-P2: fructose-2,6-biphosphate; TIGAR: TP53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator; G3P: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; PGK1: phosphoglycerate kinase 1; 3PG: 3-phosphoglycerate; PDH: pyruvate dehydrogenase; PDK: pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase; LDH: lactate dehydrogenase; MCT: monocarboxylate transporter; G6PD: glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; 6P-gluconolactone: 6-phosphogluconolactone; 6P-gluconate: 6-phosphogluconate; 6PGD: 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase; Ru5P: ribulose-5-phosphate; R5P: ribose-5-phosphate; TKT: transketolase; TALDO: transaldolase; PHGDH: phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase; PAST: phosphoserine aminotransferase; 3P-serine: 3-phosphoserine; PSPH: phosphoserine phosphatase; α-KG: α-ketoglutarate; SHMT: serine hydroxymethyl transferase; UDP-GlcNAc: uridine diphospho-N-acetylglucosamine; PI3K/Akt: phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B; mTORC1: mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; Myc: c-Myc; KRAS: Kirsten Ras GTPase; HIF1α: hypoxia-inducible factors 1α; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; PTEN: phosphate and tension homolog; Nrf2: nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2; PLK3: polo-like kinase 3; HSP90: Heat shock protein 90; STAT3: signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.