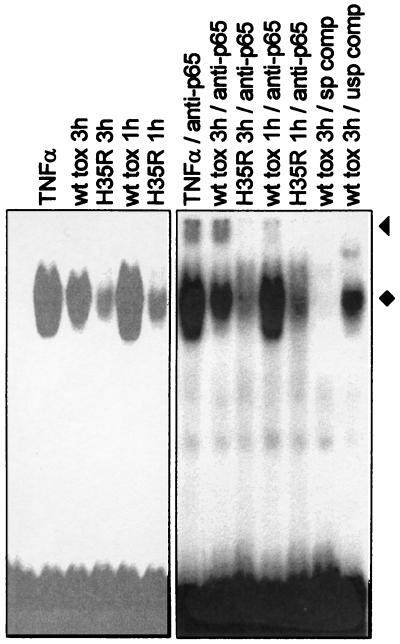
FIG. 3.
Toxin treatment activates NF-κB. EMSAs were performed with extracts from THP-1 cells treated for 1 or 3 h with wild-type (wt) or H35R toxin. The specificity of complex formation was assessed by the addition of specific (sp) or unspecific (usp) unlabeled competitor oligonucleotides; an oligonucleotide carrying an AP-1 binding site (Promega) served as an unspecific competitor in this experiment. The presence of p65 in lysates from toxin-treated cells was demonstrated by supershift induction with specific antibodies (anti-p65); supershifted bands are marked with a triangle. The NF-κB complexes are marked with a diamond. Data were derived from the same gel, but different scanning parameters were chosen. A variety of antibodies of irrelevant specificity and several other oligonucleotides encompassing binding sites for transcription factors other than NF-κB were also tested and were found to have no effect on the formation of the NF-κB complex.