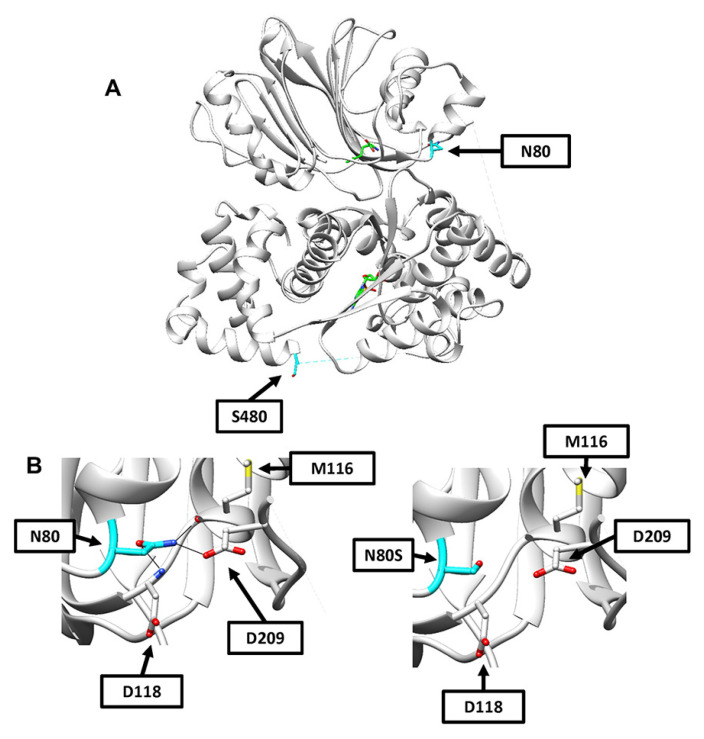
Figure 2.
Computational models of N80S and S480F variants. (A) A model of the entire human ASNS crystal structure showing the locations of N80 and S480 in cyan. Glutamine is shown in the N-terminal binding site and AMP in the C-terminal binding site, with both backbones in green, nitrogen atoms in blue, oxygen atoms in red, and phosphorous in orange. (B) Shown in the (left) panel is a close-up of the region containing N80 and showing predicted hydrogen bonding interactions with M116 (2.9 angstroms), D209 (2.9 angstroms), and D118 (2.9 angstroms). Shown in the (right) panel is the same region now displayed with the most probable N80S rotamer in place. Increased distances lead to the absence of hydrogen bonding predictions between N80S and M116 (3.9 angstroms), D209 (3.9 angstroms), and D118 (3.6 angstroms).