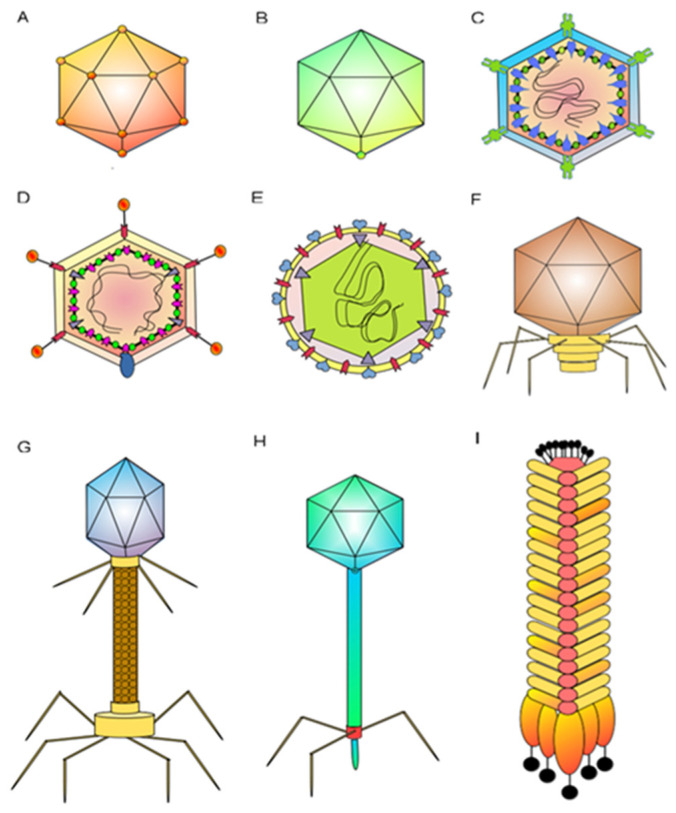
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the most commonly studied phages [16]: (A) levivirus MS2 has a capsid with icosahedral symmetry and a size of about 26 nm; (B) microvirus ϕX174 is a non-evolved icosahedral capsid about 30 nm in size; (C) podovirus T7 is a non-evolved icosahedral capsid about 60 nm in size; (D) tectivirus PRD1 is a non-enveloped icosahedral capsid with a size of about 66 nm; (E) cystovirus phi6 is an enveloped spherical virion 85 nm in diameter; outer and inner capsids have icosahedral symmetry; (F) corticovirusPM2 is an icosahedral capsid 56 nm in diameter; (G) myovirus T4 is non-enveloped, with a morphological head–tail structure about 110 nm in length; (H) siphovirus T5 is non-enveloped, with a head–tail structure; head is about 60 nm in diameter; and (I) inovirus M13 is non-enveloped, with rods of filaments 7 nm in diameter and 700 to 2000 nm in length.