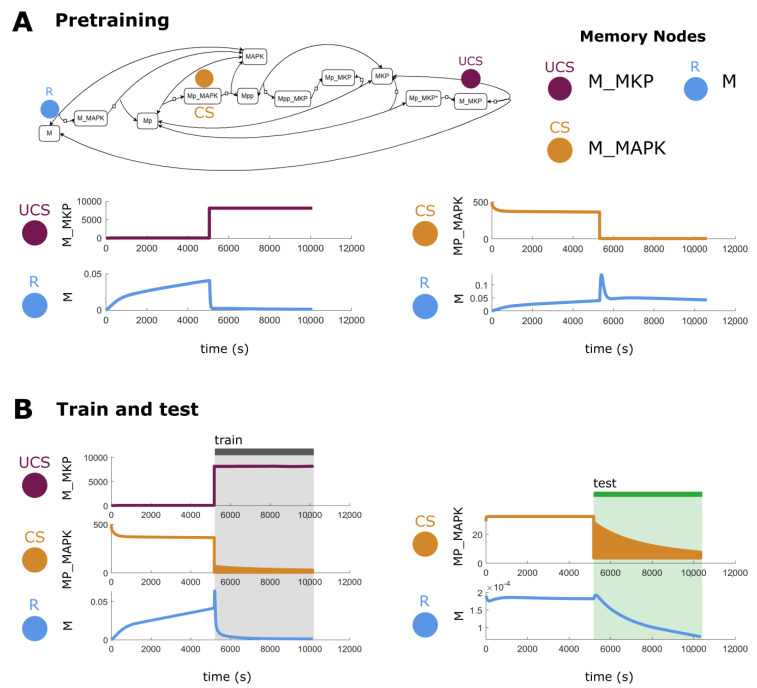
Figure 4.
Associative memory in a biological network. (A) An example of associative memory in a potential memory model derived from a biological model from [75]. This particular memory model passes the pretest—UCS stimulation leads to change in R while a stimulation of CS does not. (B) To train the model towards a response in R from a stimulation in CS, the UCS and CS are stimulated at the same time, upregulated and downregulated, respectively. After, the circuit is tested and now stimulation of the CS (downregulation) causes lasting change in R. The colors under the yellow line in both training and testing periods are meaningless and are artifacts due to the integrator used.