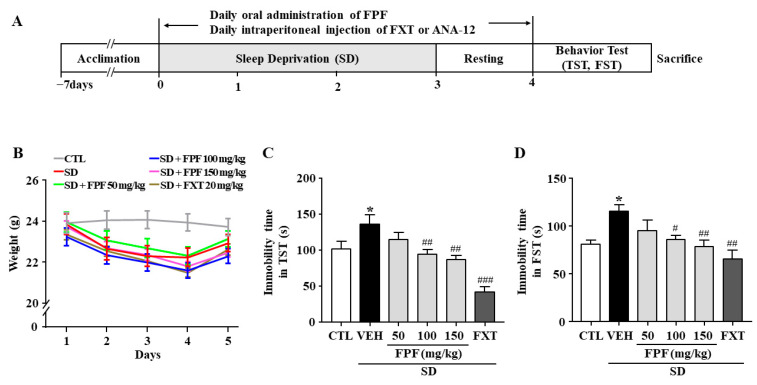
Figure 1.
Effects of FPF on SD stress-induced depression-like behavior in mice. (A) Scheme for experimental procedures. (B) Body weight (two-way ANOVA: Interaction: F(20, 210) = 0.5886, p = 0.9182; Days: F(4, 210) = 10.89, p < 0.0001; Group: F(5, 210) = 11.52, p < 0.0001). (C,D) Immobility times in the TST (C) and FST (D). TST (one-way ANOVA: F(5, 61) = 11.59, p < 0.0001); FST (one-way ANOVA: F(5, 57) = 4.537, p = 0.0015). Mice were exposed to SD-induced stress for 72 h. Mice were treated with FPF (50, 100, 150 mg/kg) by oral administration or FXT (20 mg/kg) by intraperitoneal injection once daily for 5 days. Values represent the mean ± standard error of the mean (n = 10). * p < 0.05 compared with the control group. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, and ### p < 0.005 compared with the vehicle group. TST: tail suspension test, FST: forced swimming test, CTL: control, VEH: vehicle, FXT: fluoxetine, FPF: fermented Perilla frutescens, SD: sleep deprivation.