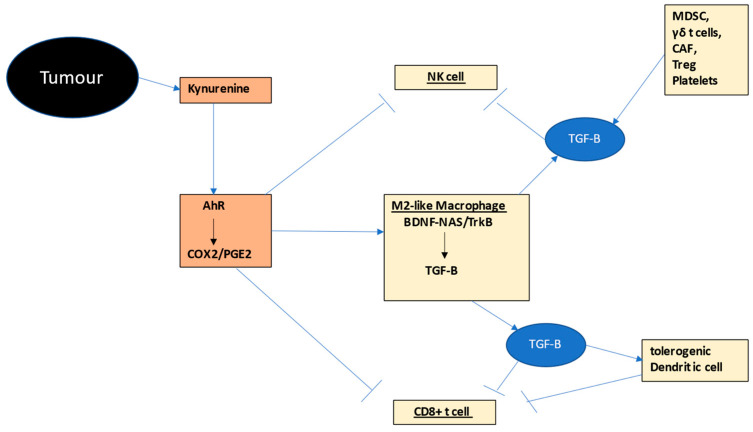
Figure 2.
Shows how tumor-(black shade) derived kynurenine activation of the AhR drives COX2/PGE2 (bronze shade) in M2-like macrophages, NK cells and CD8+ t cells (other tumor microenvironment cells in gold shade). PGE2 in macrophages induces TrkB activation by BDNF and likely by NAS, thereby increasing TGF-B (blue shade), which then induces ‘exhaustion’ in NK cells and CD8+ t cells, as well as a tolerogenic dendritic cell, the latter further suppressing CD8+ cell activation. Numerous other tumor environment cells, including MDSCs, γδ t cells, CAF, Treg and platelets also release TGF-B. The AhR therefore interacts with other tumor fluxes, such as glutamate and ATP (Figure 1), to change the NF-kB and YY1 activation by increasing the NAS/melatonin ratio, with consequences including TGF-B release from macrophages, reinforcing NK cell and CD8+ t cell ‘exhaustion’. The NAS/melatonin ratio may therefore be an important determinant of classical processes underpinning ‘immune-checkpoint’ induction. Abbreviations: AhR: aryl hydrocarbon receptor; BDNF: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; CAF: cancer-associated fibroblasts; COX: cyclooxygenase; CYP: cytochrome P450; MDSC: myeloid-derived suppressor cell; NAS: N-acetylserotonin; NF-kB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NK: natural killer; PGE2: prostaglandin E2; TGF: transforming growth factor; Treg: regulator t cell; TrkB: tyrosine receptor kinase B; YY1: yin yang 1.