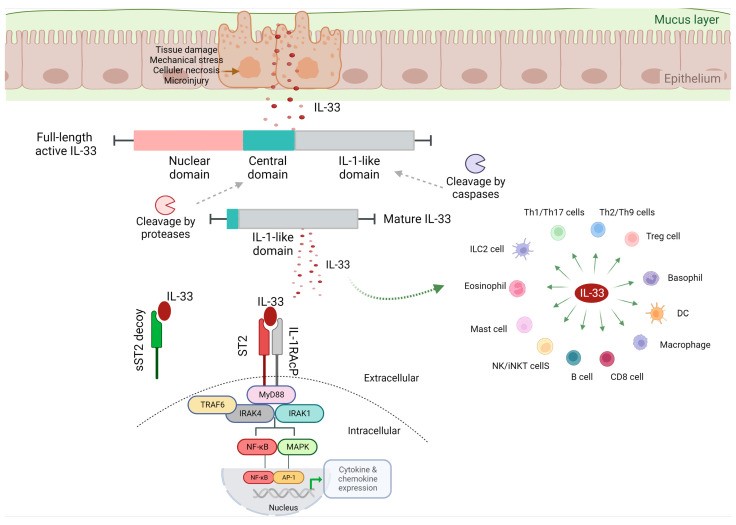
Figure 2.
Activation of IL-33/ST2 signaling. Full-length IL-33 is composed of an N-terminal nuclear domain and a C-terminal IL-1-like cytokine domain, divided by a central domain. IL-33 signals through a great variety of immune cells promoting their function. Binding of IL-33 to sST2 decoy receptor prevents the ST2/IL-33 signaling, whereas binding of IL-33 to ST2 results in the activation of the transcription factor NF-κB and the MAP kinases, leading to related-gene transcription. This figure was created with BioRender (https://biorender.com (accessed on 29 November 2022)). IL-33, interleukin-33; ST2, suppression of tumorigenicity 2; sST2, soluble ST2; IL-1RAcP, IL-1 receptor accessory protein; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response 88; TRAF6, tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6; IRAK 1, interleukin receptor-associated kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinases; AP-1, activator protein 1; Th1 cells, T helper 1 cells; Treg cells, T regulatory cells; DC cells, dendritic cells; CD8 cells, cytotoxic T cells; NK cells, natural killer cells; iNKT cells, invariant natural killer T cells; ILC2 cells, group 2 innate lymphoid cells.