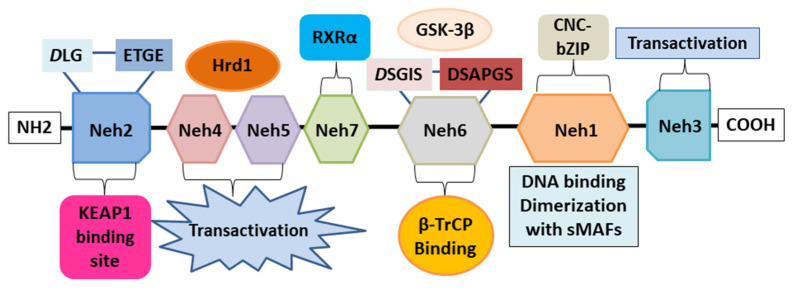
Figure 2.
The structural architecture of Nrf2. The structure of Nrf2 contains seven domains, Neh domains, Neh1-Neh7. Neh1 contains a bZip motif, where the basic region is responsible for DNA binding and the zip dimerizes with other binding partners such as sMAFs. Neh2 contains ETGE and DLG motifs, involved in the interaction with Keap1 and subsequent Keap1-mediated proteasomal degradation. Neh3, Neh4, and Neh5 domains are transactivation domains of Nrf2. In particular, Neh4 and five domains interact with the Hrd1 responsible for Nrf2 degradation. The Neh6 domain contains two redox-independent degrons, DSGIS and DSAPGS, that bind to the E3 ubiquitin ligase β-TrCP involved in the Nrf2 degradation in oxidatively stressed cells. The neh7 domain mediates the interaction with RXRα, which represses Nrf2 activity. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2: Nrf2; Nrf2-ECH homology: Neh; basic region leucine zipper: bZip; Cap’n’Collar: CNC; small muscleaponeurotic fibrosarcoma: sMAF; Kelch-like erythroid cell-derived protein with CNC homology-associated protein 1: Keap1; β-transducing repeat-containing protein: β-TrCP; retinoic X receptor alpha: RXRα; Glycogen synthase kinase-3: GSK-3β; HMG-CoA reductase degradation 1: Hrd1.