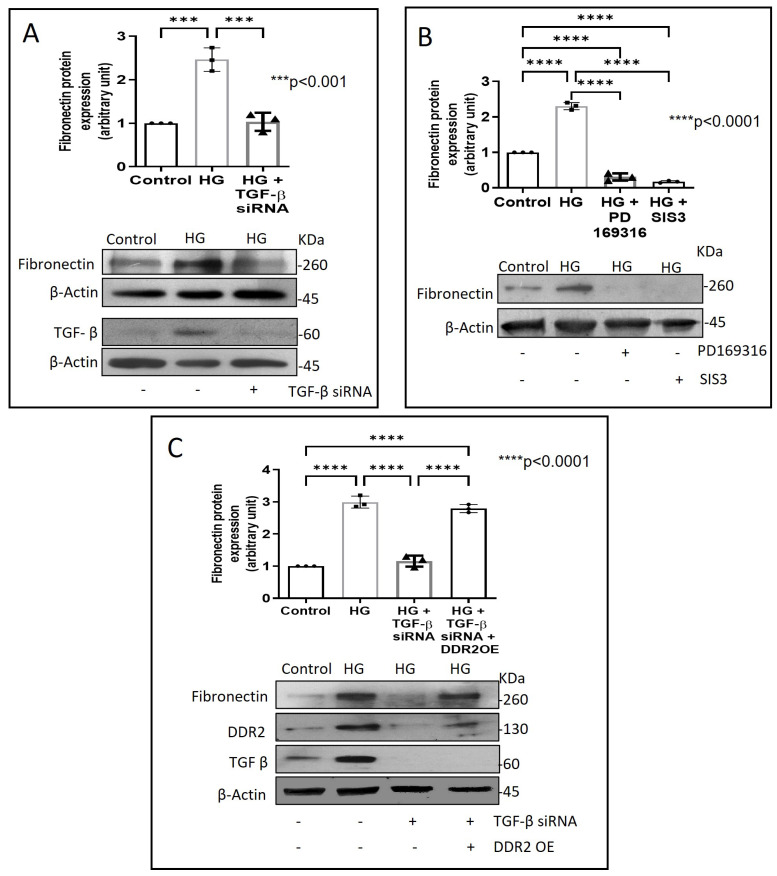
Figure 5.
DDR2 acts downstream of TGF-β1 to regulate Fibronectin expression. (A) Cells were transiently transfected with TGF-β1 siRNA 1 and 2 (5 pmol) (indicated by (+) sign) or scrambled siRNA (5 pmol) (indicated by (−) sign) prior to treatment with HG for 12 h. Protein was isolated and subjected to western blot analysis for detection of Fibronectin, with β-Actin as loading control. Validation of TGF-β1 knockdown is also shown. (B) Sub-confluent, quiescent cultures of vascular adventitial fibroblasts in M199 were pre-treated with SMAD2 inhibitor, PD169316, or SMAD3 inhibitor, SIS3, for 1 h and subsequently with HG for 12 h. Following treatment with HG, protein was isolated and subjected to western blot analysis for detection of Fibronectin, with β-Actin as loading control. 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB) reagent was used for detection of β-Actin and brightness/contrast was adjusted uniformly to match with other blots. (C) Cells were co-transfected with DDR2 cDNA plasmid (1µg) (indicated by (+) sign) or empty plasmid (1µg) (indicated by (−) sign) and TGF-β1 siRNA 1 and 2 (5 pmol) (indicated by (+) sign) or scrambled siRNA (5 pmol) (indicated by (−) sign) (lipofectamine 2000-complexed) for 8 h in OptiMEM. After a recovery period of 12 h, the cells were subjected to HG for 12 h. Following treatment with HG, protein was isolated and subjected to western blot analysis for detection of Fibronectin, with β-Actin as loading control. Validation of DDR2 OE and TGF-β1 knockdown are also shown. 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB) reagent was used for detection of β-Actin and brightness/contrast was adjusted uniformly to match with other blots. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (standard error of mean). The groups were analysed by one-way ANOVA (p ≤ 0.05) and Tukey’s multiple comparisons (p ≤ 0.05). Significant comparisons along with their p values are depicted in the Figure. The data are representative of three independent experiments, n = 3.