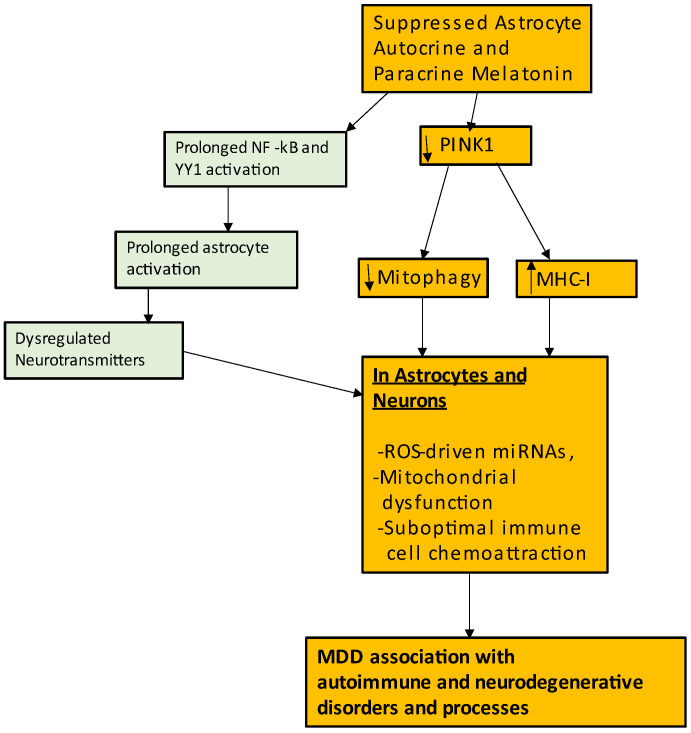
Figure 3.
The suppression of astrocyte autocrine and paracrine melatonin also impacts on the regulation of processes associated with autoimmunity. Decreased autocrine and paracrine melatonin in astrocytes and neurons, respectively decreases mitochondrial membrane associated PINK1, leading to suppressed mitophagy of dysfunctional mitochondria and increased MHC-1. The associated increase in ROS alters patterned miRNAs and gene expressions, leaving cells more vulnerable to challenge. This may include alterations in the chemoattraction of immune cells. The astrocyte melatonergic pathway may therefore also be a major mediator of the association of MDD with autoimmune disorders as well as with autoimmune processes, such as MHC-1, which is highly expressed in the MDD brain. Abbreviations: MHC-I: major histocompatibility complex class I; NF-kB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; PINK1: PTEN-induced kinase 1; ROS: reactive oxygen species; YY1: yin yang 1.