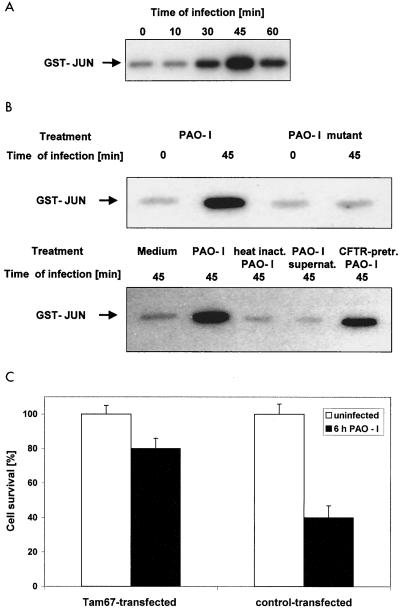
FIG. 2.
P. aeruginosa PAO-I induces activation of JNK. (A) P. aeruginosa PAO-I infection of Chang epithelial cells induces rapid activation of JNK. Cells were infected with PAO-I for the indicated time and lysed, JNK was immunoprecipitated, and kinase activity was determined by phosphorylation of GST-c-JUN followed by separation by SDS-PAGE, blotting, and autoradiography. Shown is a blot representative of three similar experiments. (B) PAO-I supernatants, heat-inactivated PAO-I, and type III secretion system-deficient P. aeruginosa PAO-I fail to activate JNK, whereas CFTR-pretreated PAO-I induced JNK activation. Cells were left uninfected or infected for 45 min as indicated. JNK activity was determined as described above. Experiments were repeated twice with similar results. (C) Transient transfection of Chang cells with Tam67 blocking JNK reduces apoptosis induced by P. aeruginosa infection. Shown is the percent survival of the cells as determined by DNA fragmentation after 6 h of infection (mean ± SD of three experiments).