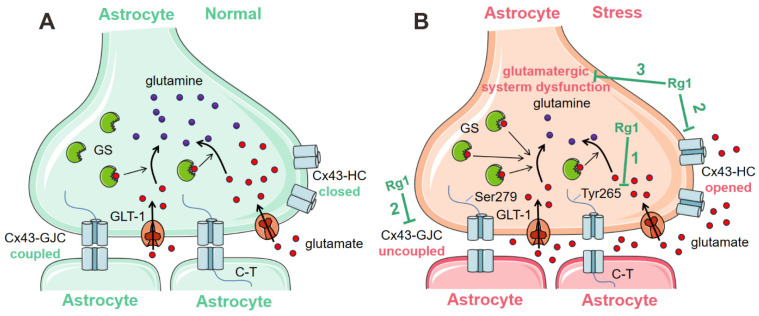
Figure 6.
Model schematic showing the antidepressant mechanism of Rg1 based on the improvement of GJC function. (A) Under physiological conditions, astrocytic Cx43 is expressed in the plasma membrane and assembled into hemichannels that remain closed. Hemichannel–hemichannel interactions induce the formation of GJC between adjacent astrocytes, which allows the exchange of ions and small molecules. Over 90% of the glutamate in the synaptic cleft is taken up by GLT-1 into astrocytes to maintain a low concentration in the synaptic cleft, and then is converted to less toxic glutamine by astrocyte-specific GS. (B) (1) CORT induces increased Ser279-phosphorylated and Tyr265-phosphorylated Cx43, which mainly contribute to the dysfunction of GJCs. Rg1 can reverse the increase of these two phosphorylated-Cx43. (2) Increased phosphorylated-Cx43 induced the dysfunction of GJCs. CORT induces the opening of hemichannels, as well, which promotes GJC disassembly further. Rg1 can inhibit hemichannel opening and ameliorate GJC dysfunction. (3) The glutamate concentration in the synaptic cleft increases due to the opening of hemichannels. Excess glutamate in the synaptic cleft results in impaired function of the astrocyte glutamatergic system, manifested by decreased total glutamate content, decreased total glutamine content, an increase in GS activities, and an increase in glutamate release and uptake. Rg1 is able to ameliorate glutamatergic dysfunction, including all of these changes. Abbreviations: CORT, corticosterone; C-T, C-terminals; GJC, gap junction channel; GS, glutamine synthetase; HC, hemichannel.