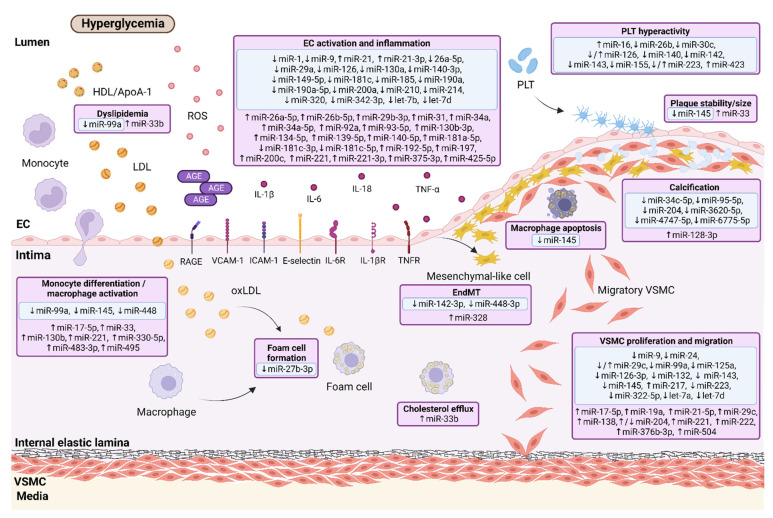
Figure 2.
MicroRNAs implicated in T2DM-related atherosclerosis. Positive/atheroprotective (in green frame) and negative/atherogenic (in violet frame) effects of miRNAs on every step of the atherosclerotic process under diabetic conditions are shown. Chronic hyperglycemia induces inflammation, and oxidative stress leading to the cascade of processes, including EC activation, migration of monocytes into the intima and their maturation into macrophages, foam cell formation by oxLDL uptake, PLT hyperactivity, VSMC proliferation and migration into the intima. Single miRNAs are also found to be engaged in EndMT, calcification, and regulation of plaque size/stability. miR—microRNA; EC—endothelial cell; EndMT—endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition; VSMC—vascular smooth muscle cell; PLT—platelet; ROS—reactive oxygen species; IL—interleukin; TNF-α—tumor necrosis factor α; IL-6R—interleukin 6 receptor; IL-1βR—interleukin 1β receptor; TNFR—tumor necrosis factor receptor; AGE—advanced glycation end-product; RAGE—receptor for advanced glycation end-products; VCAM-1—vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; ICAM-1—intercellular adhesion molecule-1; HDL—high-density lipoprotein; LDL—low density lipoprotein; ApoA-1—apolipoprotein A-1; ox-LDL—oxidized low-density lipoprotein. ↑ upregulation; ↓ downregulation. Created with BioRender.com.