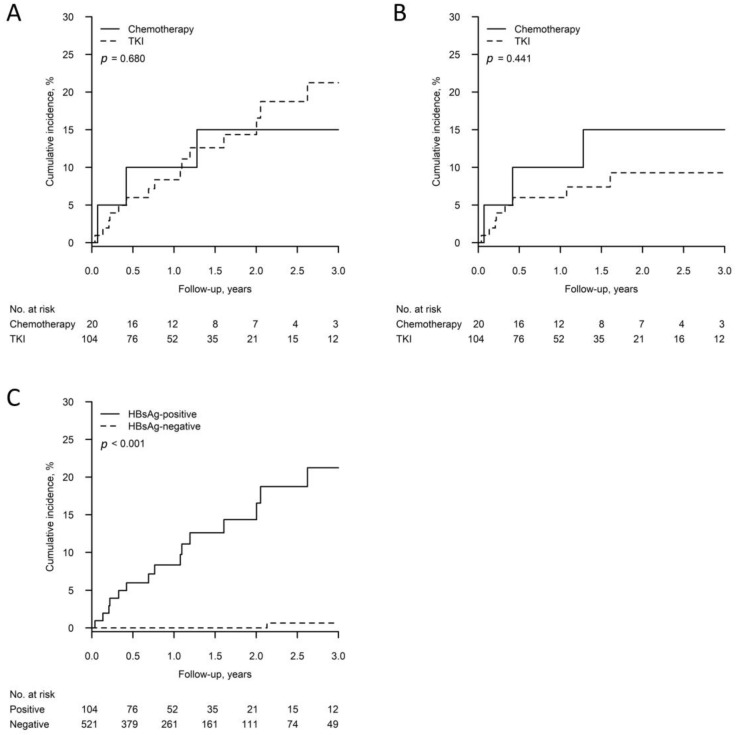
Figure 2.
(A) Cumulative incidence of HBV reactivation in HBsAg-positive patients without prophylactic NUC who received chemotherapy or tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI). (B) Comparison of cumulative HBV-related hepatitis incidence between HBsAg-positive patients without prophylactic NUC receiving chemotherapy and TKI. (C) Comparison of cumulative HBV reactivation incidence in patients receiving first-line TKI without prophylactic NUC between HBsAg-positive and HBsAg-negative groups. TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor.