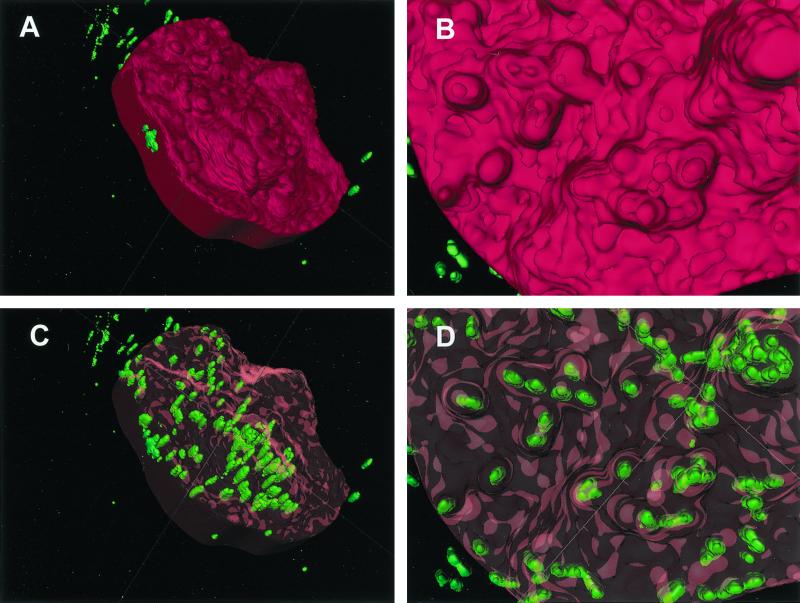
FIG. 2.
Three-dimensional reconstruction of a buccal epithelial cell from a single subject, hybridized with the EUB338 probe. (A) Surface contour of the target cell, with the surface rendered opaque in red. Editing of an adjoining cell out of this image accounts for the regular border on the left side. Green bacteria which appear to be extracellular were in fact contained within the cells that were edited out. (B) A close-up view of the opaque host cell surface reveals a very irregular contour. (C) The surface of the target cell is rendered transparent with red highlights. This reveals clusters of green bacteria which appear to be intracellular, since they cannot be seen otherwise. The elongated appearance of the bacterial cells may be an artifact of poorer resolution along the z axis. According to the scoring system described in the text, this cell would be consistent with a ranking of >100 bacteria. (D) The close-up transparent view shows that some surface protuberances were associated with bacterial clusters. However, bacteria in those clusters seemed to be located below the surface.