Figure 3.
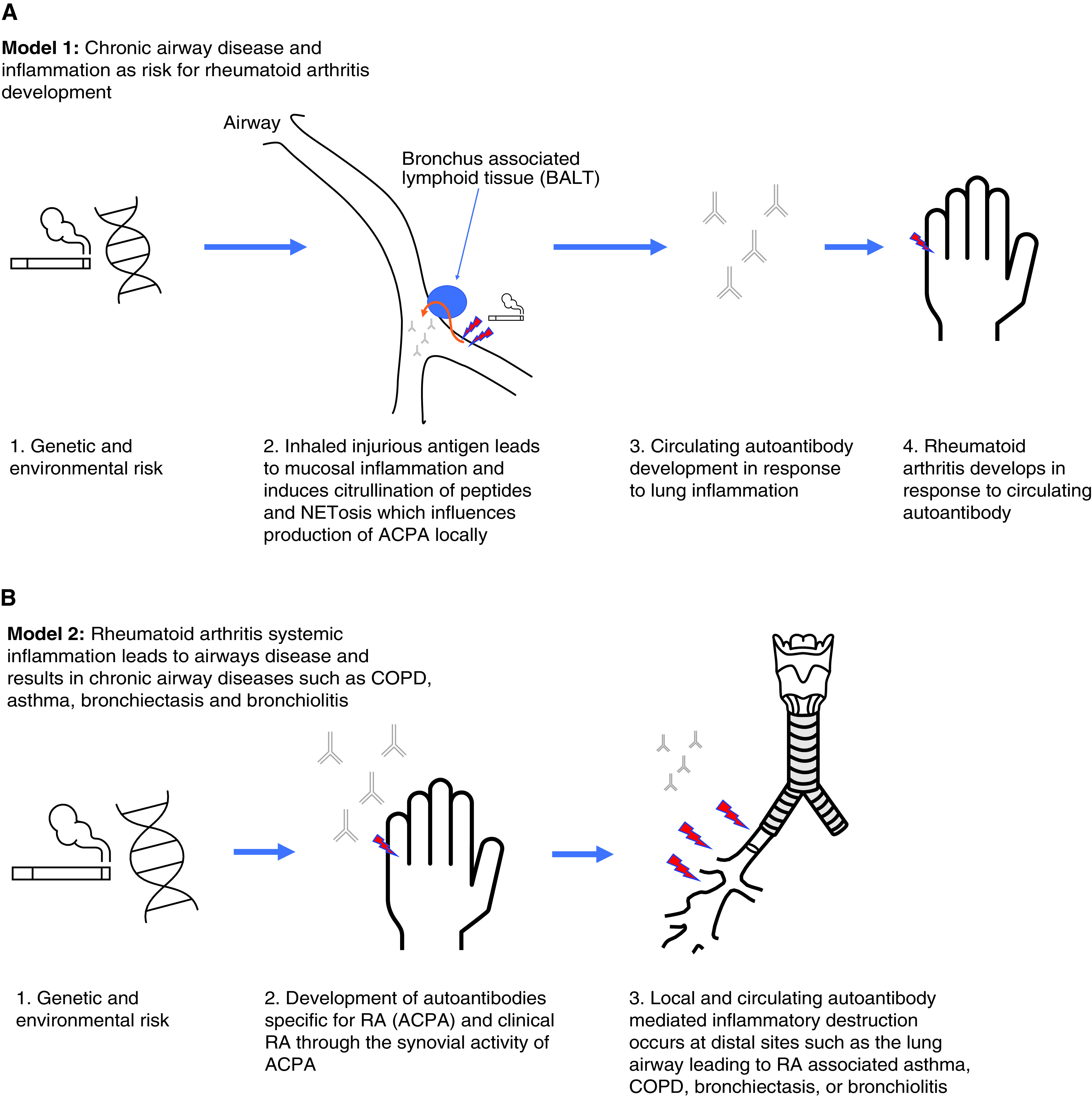
(A) Model 1: Chronic airway disease and inflammation as risk for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) development. Data that support model 1 of development of antibodies to citrullinated protein antigens (ACPAs) in chronic lung disease are found in References 7, 19, 20, 35, 38, 39, 45, 79, 80, 83, 85, and 92. (B) Model 2: Airway diseases such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), bronchiectasis, and bronchiolitis result as a direct manifestation of RA autoantibody-mediated inflammation and represent a unique autoimmune endotype of airway disease. Data that support model 2 of RA-mediated lung inflammation causing airway phenotypes are found in References 28, 46, 56, 68, and 93–95. NETosis = neutrophil extracellular trap formation.
