Figure 4.
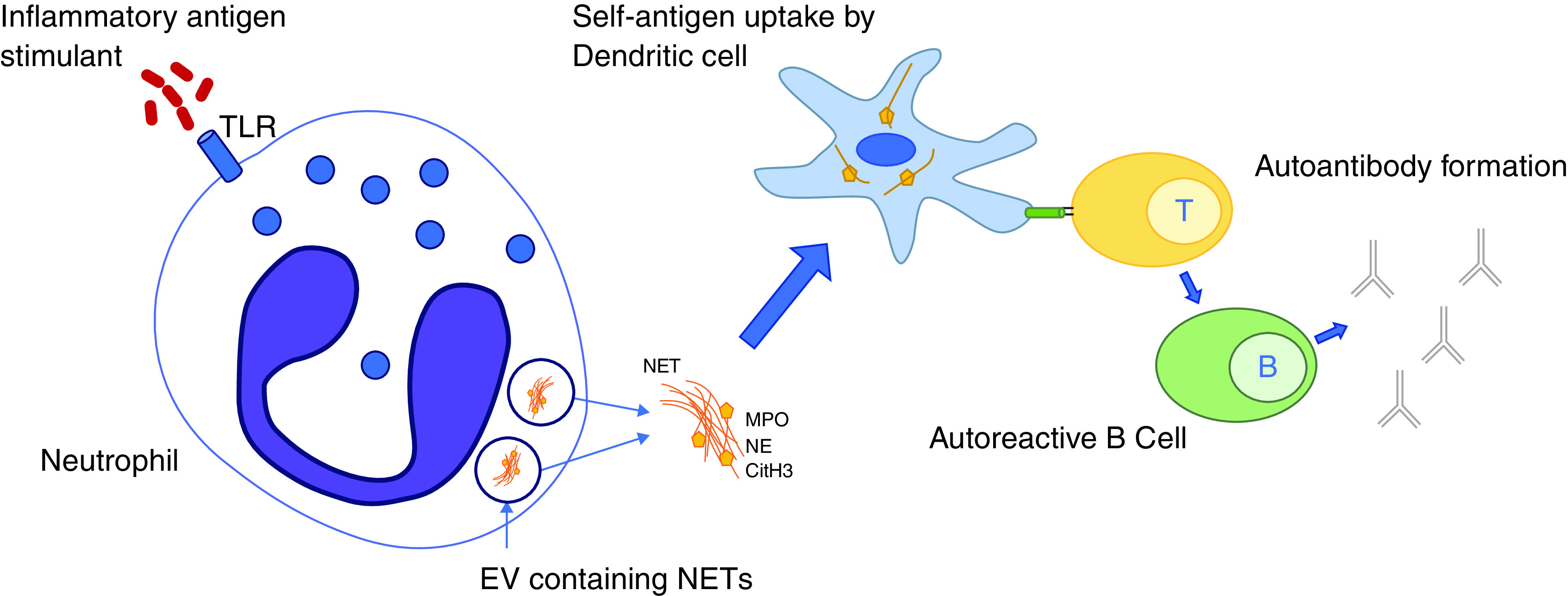
Neutrophil extracellular trap formation (NETosis) occurs when an antigenic stimulus, such as bacterial infection, stimulates the release of decondensed nucleolar material from the neutrophil, which, in addition to innate immune function capabilities, contains self-antigens. These self-antigens are then taken up by dendritic cells and through T and B cell interactions lead to the production of autoantibodies such as antibodies to citrullinated peptide antigens (ACPAs). CitH3 = citrullinated histone 3; EV = extracellular vesicle; MPO = myeloperoxidase; NE = neutrophil elastase; NET = neutrophil extracellular trap; TLR = Toll-like receptor.
