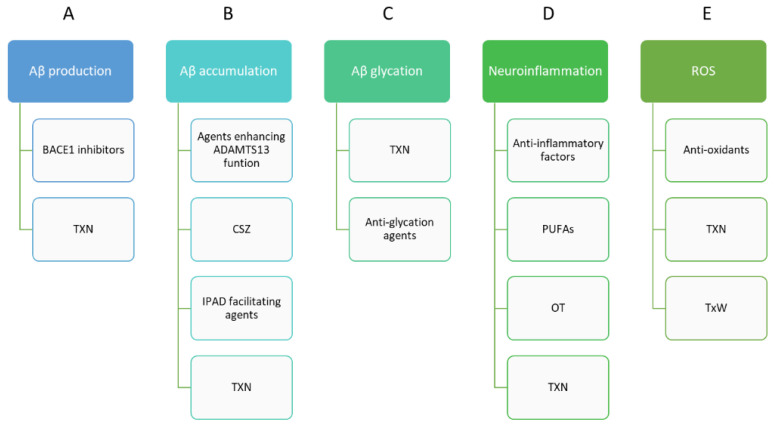
Figure 1.
Pathological implications of amyloid-β and its role in potential therapeutic approaches for Alzheimer’s disease. In AD treatment, BACE1 inhibitors inhibit Aβ production (A). Another option is taxifolin (TXN) which, with its pleiotropic beneficial effects, suppresses the production and glycation of Aβ; also, it is effective in reducing detrimental Aβ accumulation (B). Anti-glycation agents could reduce the accumulation of cytotoxic Aβ oligomers (Aβ glycation) (C). Agents that facilitate the formation of mature fibers would also be effective in facilitating the Intramural Peri-Arterial Drainage (IPAD) pathway or enhancing ADAMTS13 function. Anti-inflammatory mediators (D) and antioxidants (E) and may also exhibit protective effects against AD. Aβ, amyloid-β; AD, Alzheimer’s disease; ADAMTS13, a disintegrin and metalloprotease with thrombospondin type I motif, member 13; BACE1, β-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme-1; CSZ, cilostazol; OT, oxytocin; PUFAs, polyunsaturated fatty acids; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TwX, Twendee X; TXN, taxifolin.