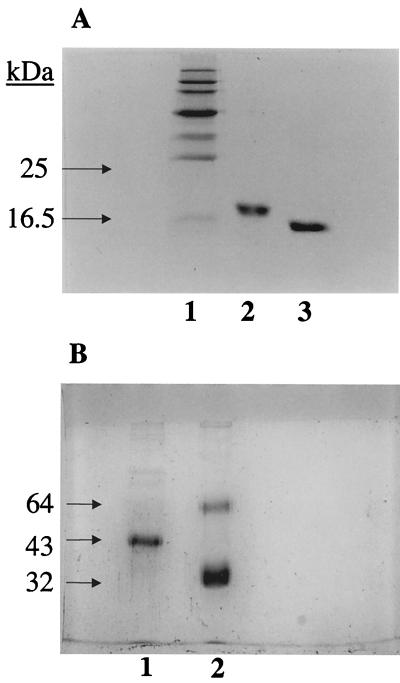
FIG. 1.
(A) SDS-PAGE (15%, wt/vol) analysis of purified preparations of rSP-D under reducing as well as nonreducing conditions (Coomassie stained). A recombinant fragment composed of the trimeric, α-helical coiled-coil neck region and three CRDs of human SP-D (rSP-D) was expressed in E. coli in the inclusion bodies and purified. The recombinant protein behaved as a homotrimer of ∼60 kDa when examined by gel filtration chromatography and chemical cross-linking (data not shown). Under reducing conditions (lane 2), the protein ran as a monomer of ∼18 kDa. No higher oligomers were seen when rSP-D was run under nonreducing conditions (lane 3), showing that the trimerization was not a result of aberrant disulfide bridges between CRD regions. rSP-D was also assessed for correct folding using circular dichroism, disulfide mapping, and the determination of its crystallographic structure in complex with maltose in the carbohydrate-binding pockets (Shrive et al., unpublished data). (B) SDS-PAGE (10%, wt/vol) analysis of purified preparations of SP-D and SP-A under reducing conditions (Coomassie stained). The majority of SP-D is composed of a 43-kDa polypeptide chain, with faint bands corresponding to dimers and trimers of the 43-kDa chain (lane 1; also confirmed by immunoblotting). Two bands are seen (lane 2), a major band corresponding to the 32-kDa polypeptide chain of SP-A, together with a proportion of nonreducible dimers (64 kDa). Traces of higher oligomers and some aggregates (confirmed by immunoblotting) can also be seen. The nonreduced preparations of SP-D and SP-A behaved on SDS-PAGE as described previously (27). All of the SP-A preparation was composed of octadecamers, as judged from gel filtration and electron microscopy studies. The exact proportions of the SP-D preparation in the form of dodecamers and higher oligomers was not established.