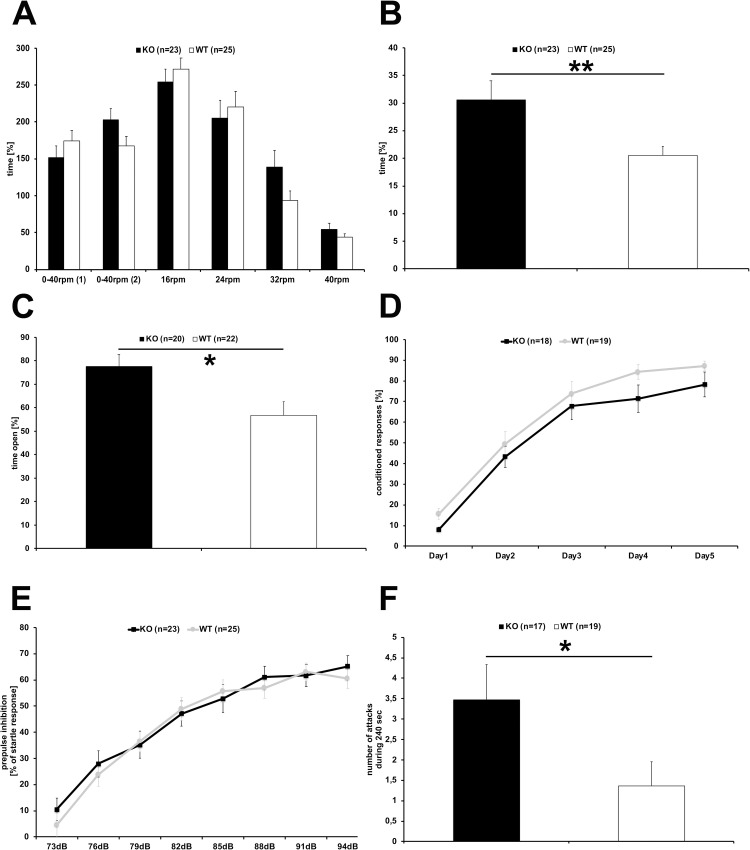
Fig 1. Behavioral assessment of BT-IgSF-deficient mice.
BT-IgSF-deficient mice and control wildtype littermates were subjected to a series of behavioral paradigms. Motor coordination tested on the rotarod (A) did not differ between BT-IgSF-deficient (black columns) and control mice (white columns). In the open field (B) BT-IgSF-deficient mice (black column) stayed significantly longer in the center compared to their wild-type littermates (white column). In the O-Maze (C) BT-IgSF-deficient mice (black columns) spend more time in the open areas compared to littermate controls (white column). In the two-way active avoidance shuttle box paradigm (D) BT-IgSF-deficient (black line) and control mice (grey line) showed similar acquisition of the task as measured by conditioned responses indicating normal associative learning. Prepulse inhibition of the startle response (E) was not affected in BT-IgSF-deficient mice (black squares) in comparison to wild type littermates (grey bullets). Male BT-IgSF-deficient mice (black column) displayed increased aggression in the intruder test (F) compared to controls (white column) measured by the number of attacks.