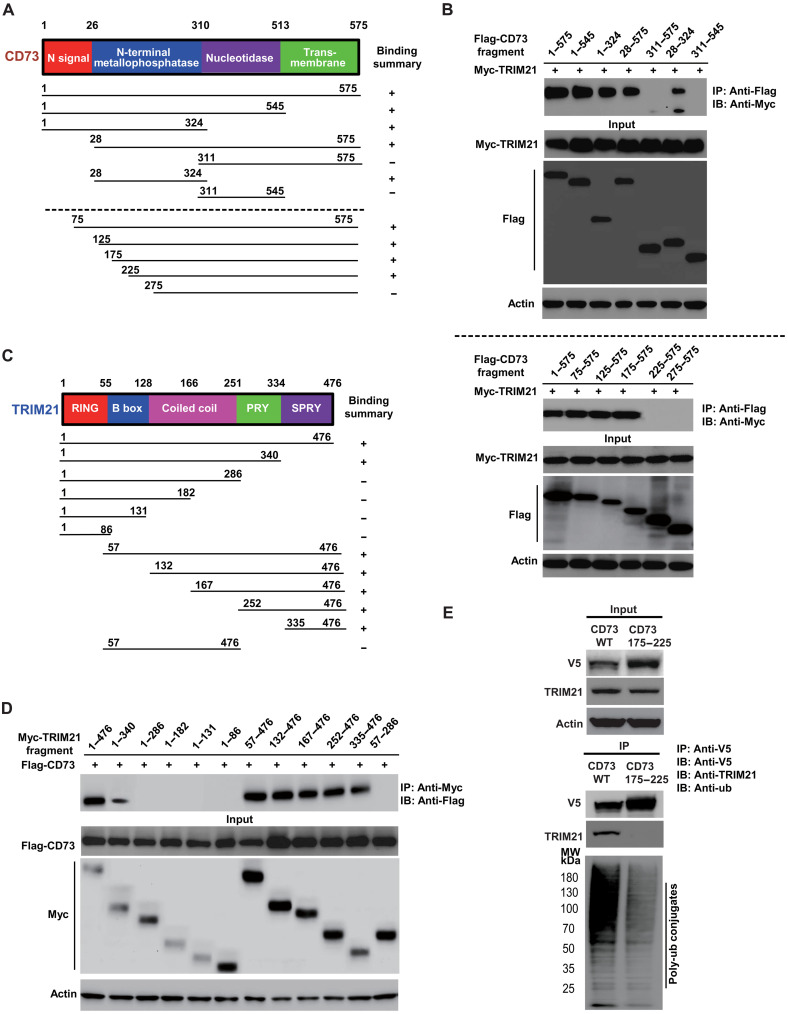
Fig. 4. Mapping of molecular regions that facilitate the interaction between CD73 and TRIM21.
(A) Schematic diagram of human CD73 domains and strategy to engineer a series of CD73 deletion fragments. (B) The interactions between TRIM21 and CD73 fragments were examined by coimmunoprecipitation experiments in HEK-293T cells. Top: Identification of amino acid stretches from 28 to 311 on CD73 mediates the interaction between CD73 and TRIM21, measured by coimmunoprecipitation with a series of Flag-tagged CD73 fragments followed by immunoblotting of coexpressed Myc-TRIM21 antibody against Myc. Bottom: Narrowing down amino acid stretches from 175 to 225 on CD73 facilitates the interaction between CD73 and TRIM21. (C) Schematic diagram of human TRIM21 domains and strategy to engineer a series of TRIM21 deletion mutants. (D) Mapping of the molecular domain on TRIM21 involving in the interaction with CD73. The interactions between CD73 and TRIM21 fragments were examined by coimmunoprecipitation experiments in HEK-293T cells. Amino acid stretches from 340 to 476 on TRIM21 (PRY/SPRY domain) were identified as the region that mediates the interaction between TRIM21 and CD73. (E) Validation of interaction domains between TRIM21 with CD73 by coimmunoprecipitation of ectopic V5-tagged CD73 176 to 225 amino acid deletion mutant in HEK-293T cells. The ubiquitylation status of CD73 and CD73 deletion mutant were also determined using an antibody against ubiquitin.