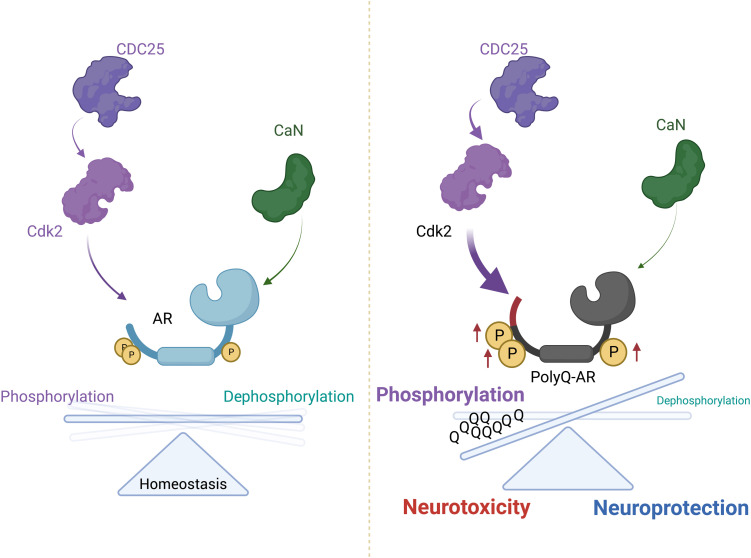
Fig. 10. Opposing effects of CDC25/CDK2 and CaN on polyQ-expanded AR neurotoxicity.
CDC25/CDK2 phosphorylate AR and contribute to toxicity in vitro and in vivo, whereas CaN removes phospho-marks in response to calcium signaling, thus modifying subcellular localization, function, and toxicity. CDK2 triggers a stress response in the brainstem, and its loss of function reduces polyQ-expanded AR phosphorylation and attenuates neurodegeneration.