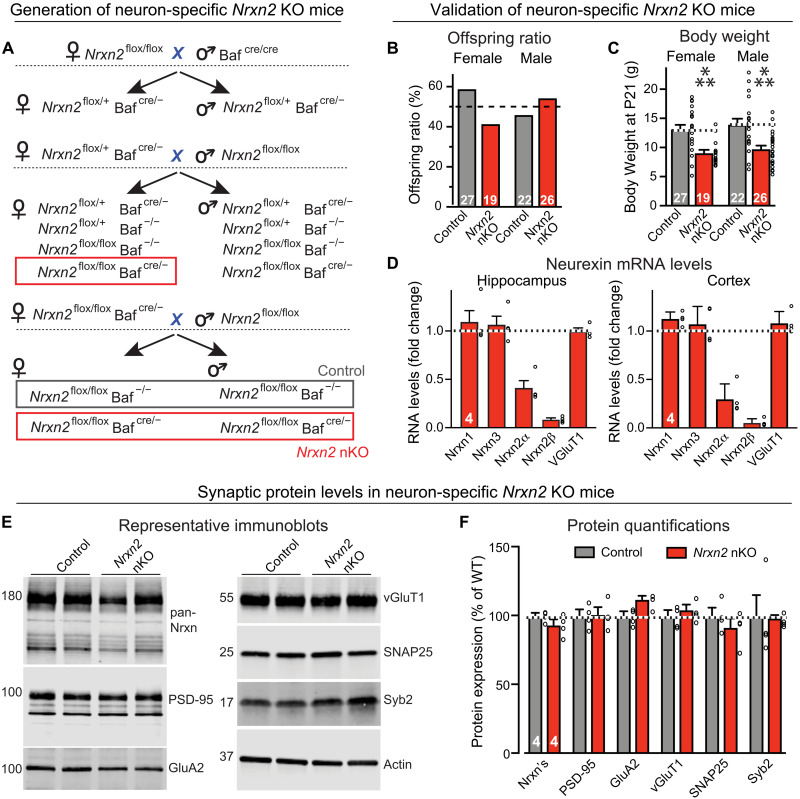
Fig. 2. The pan-neuronal deletion of Nrxn2 (Nrxn2 nKO) partly decreases Nrxn2 mRNAs but does not affect the levels of other mRNAs or protein levels.
(A) Breeding strategy for generating pan-neuronal Nrxn2 KO (Nrxn2 nKO) mice by crossing Nrxn2 cKO mice with Baf53b-Cre mice (47). (B) The Nrxn2 nKO does not impair mouse survival. The graph depicts the genotype distribution in surviving offspring from matings of homozygous Nrxn2 cKO (control) and Nrxn2 nKO mice, with an expected 50% offspring survival ratio for Nrxn2 cKO control and Nrxn2 nKO mice, assessed at postnatal day 21 (P21). (C) Body weight of the mice analyzed in (B). (D) Quantification of the indicated neurexin mRNA levels in the hippocampus and cortex of littermate Nrxn2 cKO control and Nrxn2 nKO mouse brains, expressed as the fraction of the mRNA levels in the nKO mice compared to controls. Note that the remaining Nrxn2α mRNA levels are higher than Nrxn2β mRNA levels because Nrxn2α but not Nrxn2β is also expressed in astrocytes and OPCs (oligodendrocyte precursor cells). (E and F) Immunoblotting analyses show that the neuron-specific Nrxn2 deletion (Nrxn2 nKO) does not significantly alter the levels of key synaptic proteins, including that of total neurexins [(E) representative blots; (F) summary graph of protein levels as determined by quantitative blotting using fluorescent secondary antibodies and Licor detection]. Data in (B) to (D) and (F) are means ± SEM; the numbers of analyzed mice or of cells per mice are shown in the bars. Statistical analyses were performed using the Mann-Whitney test comparing KO to WT, with ***P < 0.001.