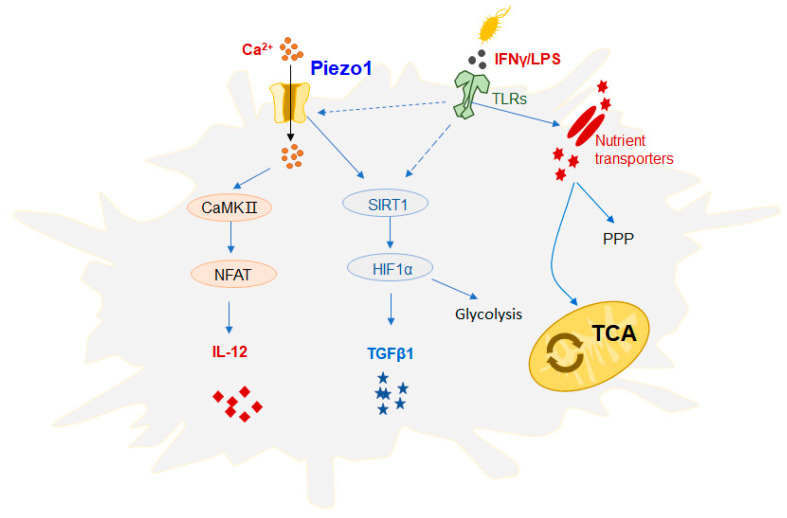
Figure 3.
Effect of Piezo1 on the function of DCs. Mechanical stimulation can activate Piezo1 signaling, regulate dendritic cell (DC) responses, and trigger inflammatory responses. Recent studies have demonstrated that DC cells growing at a high rigidity in vitro show significantly increased proliferation, activation cytokine production, and a significant upregulation of glucose metabolism pathway flux, including the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle) and pentose phosphate pathway (PPP). In addition, studies have found that Piezo1 can integrate the SIRT1-HIF1α glucose metabolism pathway and the Ca2+-calmodulin-nuclear transcription factor (NFAT) pathway to govern the secretion of DC cytokines. The DC mechanization of Piezo1 stimulated by mechanical force or inflammatory signaling regulates the mutual differentiation of Th1 and regulatory T cells (Treg cells) in the inhibition of tumor growth. Piezo1 is present in response to both inflammation and mechanical stimulation, which can mediate changes in ion concentration and metabolic signals in the cellular environment and alter its function, thus playing an important role in disease progression.