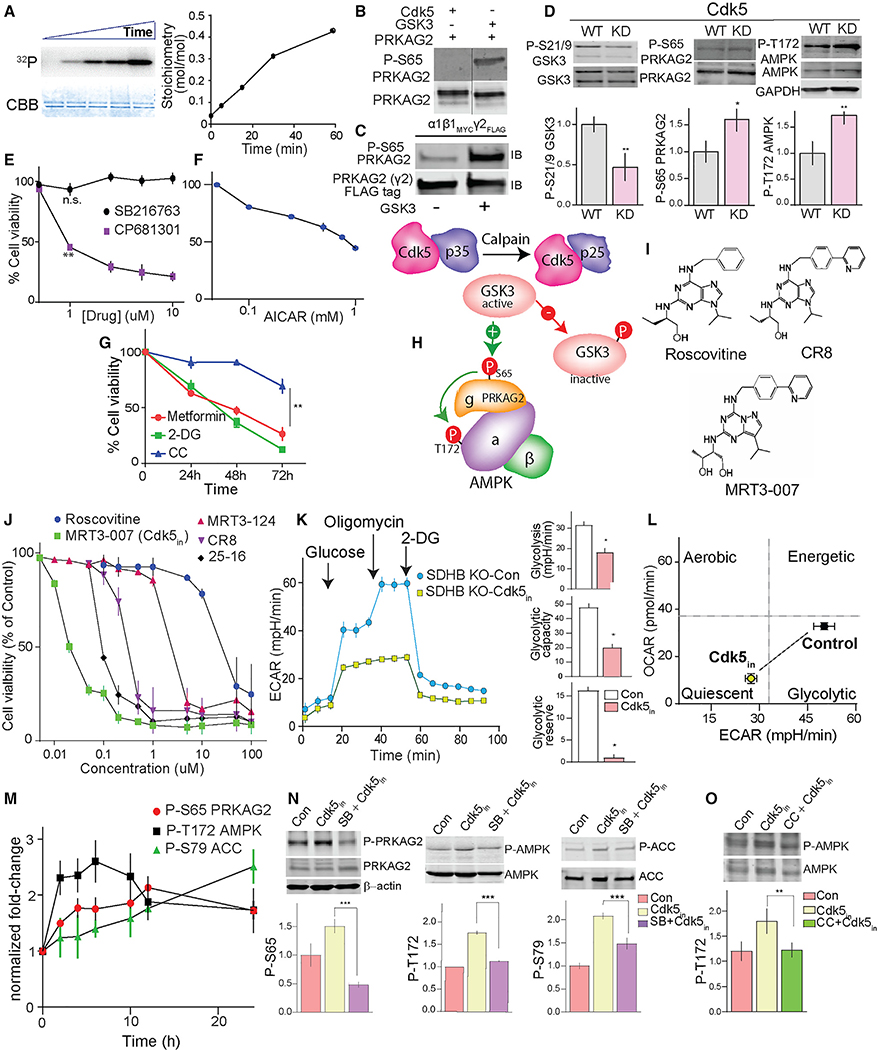
Figure 6. Targeting Cdk5 to regulate the P-PRKAG2/P-AMPK cascade.
(A) In vitro phosphorylation of recombinant PRKAG2 by GSK3, with time-dependent 32P incorporation and Coomassie-Brilliant Blue (CBB) stained protein shown with stoichiometry.
(B) Immunoblots showing GSK3 but not Cdk5 phosphorylates Ser65 PRKAG2 in vitro.
(C) Immunoblots of recombinant AMPK holoenzyme trimeric complex (α1β1γ2) phosphorylated by GSK3β.
(D) Effects of ectopic expression of WT versus kinase-dead (KD) Cdk5 on the levels of phosphorylation sites as shown.
(E) Dose-dependent effects of GSK3 (SB216763, 24 h) versus CDK5 inhibition (CP681301, 24 h) on SDHB KO hPheo1 cell viability.
(F) Plot showing dose-dependent effect of AMPK activator AICAR on cell viability (24 h).
(G) Time-dependent effects of AMPK activators, metformin (20 mM), 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG, 20 mM), and AMPK inhibitor, compound C (CC; 10 μM) on KO hPheo1 cell viability. n = 3, values are mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared by one-way ANOVA.
(H) Schematic of signaling mechanism showing aberrant CDK5-GSK3β crosstalk and deregulation of downstream phospho-dynamics of AMPK pathway.
(I) Chemical structures of Cdk5 inhibitors, as indicated.
(J) Dose-response effects of five different Cdk5 inhibitors on cell viability of hPheo1. n = 4.
(K) Glycolytic profile of SDHB KO cells treated with or without MRT3–007 [Cdk5in], 25 nM for 12 h (left). Plots comparing basal glycolysis rate, glycolytic capacity, and glycolytic reserve between control versus Cdk5in (right).
(L) Bioenergetic phenotype of KO cells in response to Cdk5in. Values are means ± SD, *p < 0.05, Student t test, n = 2 (10 replicates per group).
(M) Immunoblot quantification showing time-dependent effect of Cdk5in on phosphorylation states as indicated, n = 3, values presented as fold change normalized with time = 0.
(N) Immunoblot analysis of the impact of GSK3 inhibitor, SB216763 (5 μM, pretreatment 10 h) on Cdk5in-induced phosphorylations.
(O) hPheo1 pre-incubated with or without CC (10 μM), immunoblot quantitation comparing effects of Cdk5in alone or in combination with CC.