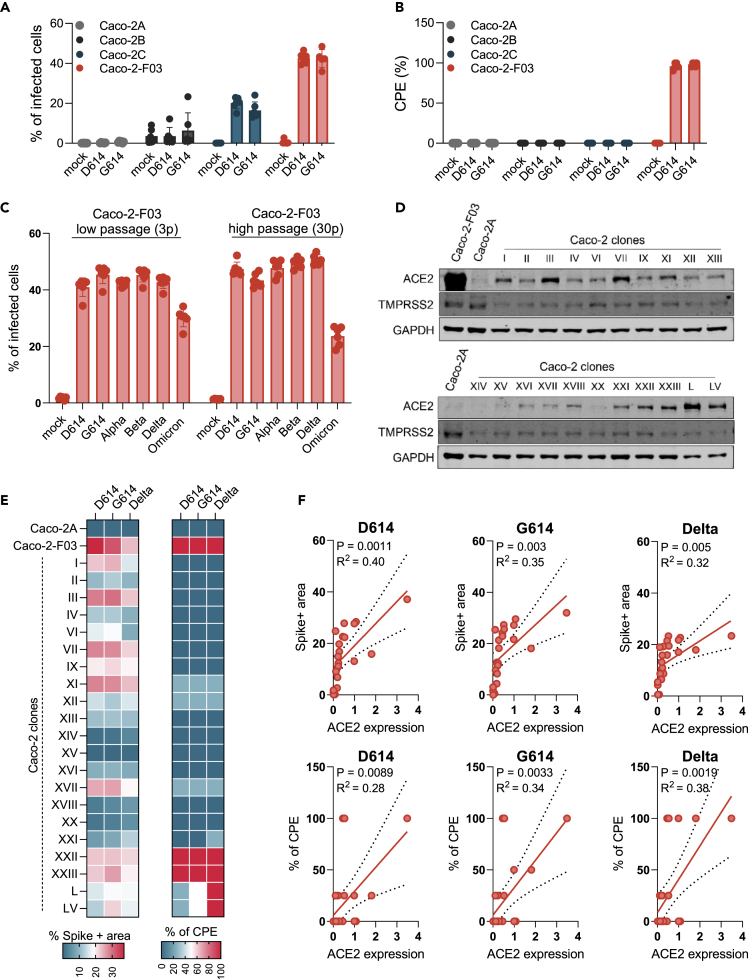
Figure 1.
Susceptibility of Caco-2 cells to SARS-CoV-2 infection
(A) Percentage of SARS-CoV-2-infected cells detected in Caco-2 cell lines from different sources infected with different SARS-CoV-2 isolates at a MOI 0.01 as determined by immunostaining for the viral spike (S protein) 48 h postinfection.
(B) Cytopathogenic effect (CPE) formation in SARS-CoV-2 (MOI 0.01)-infected Caco-2 cell lines from different sources as determined 48 h postinfection.
(C) Susceptibility of Caco-2-F03 cells to a broad range of SARS-CoV-2 isolates after different times of cultivation. Cells had been frozen at passage 14 and were resuscitated and cultivated for a further 30 passages. SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility was determined by immunostaining for S 48h after SARS-CoV-2 (MOI 0.01) infection 3 and 30 passages post-resuscitation.
(D) ACE2 and TMPRSS2 levels in Caco-2-F03, Caco-2A, and single-cell derived clones from Caco-2A.
(E) Susceptibility of Caco-2A clones to selected SARS-CoV-2 isolates as indicated by immunostaining for S and CPE formation in SARS-CoV-2 (MOI 0.01)-infected cells 48 h postinfection.
(F) Correlation of S staining and CPE formation with cellular ACE2 levels. Correlations were determined using the Pearson correlation coefficient.
Results are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation.