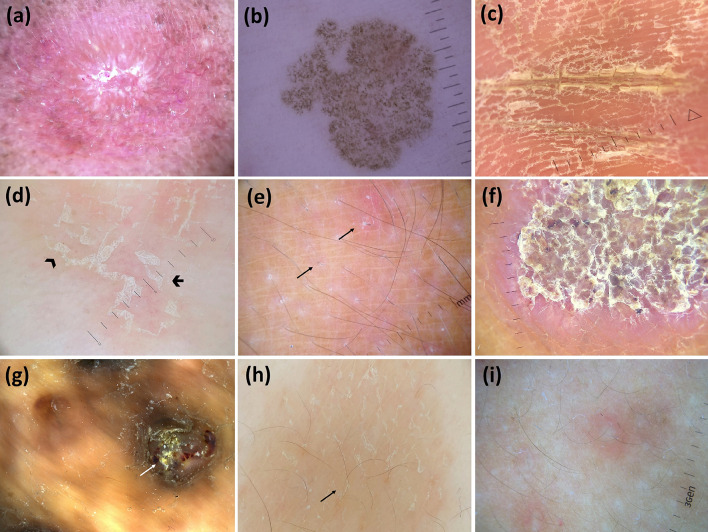
Fig. 5.
Dermoscopic images (×10 magnification): sporotrichosis [follicular plugs (yellow tears) and unfocused linear vessels over an orange-erythematous background] (adapted from Dermoscopy in General Dermatology for Skin of Color, Errichetti E, Lallas A, eds. CRC Press 2021) (a); tinea nigra (wispy brown pigment with spicule forming filamentous/reticular pattern not following dermatoglyphic lines) (adapted from “Dermoscopy in General Dermatology, Lallas A, Errichetti E, Ioannides D, eds. CRC Press 2018) (b); tinea manuum (white scales in palmar furrows) (c); tinea corporis (peripheral white scaling with both inner—arrowhead—and outer free edge—arrow) (d); tinea incognito (perifollicular white scaling and broken hairs—arrows) (e); chromoblastomycosis (reddish black–brown dots and white scaling with a peripheral yellow erythematous rim) (adapted from Dermoscopy in General Dermatology for Skin of Color, Errichetti E, Lallas A, eds. CRC Press 2021) (f); mycetoma (yellow globules, white scales, and blood spots) (adapted from Dermoscopy in General Dermatology for Skin of Color, Errichetti E, Lallas A, eds. CRC Press 2021) (g); pityriasis versicolor (white scaling in the skin furrows and brownish background) (h); and pityrosporum folliculitis (white round follicular globule surrounded by an erythematous halo) (i)