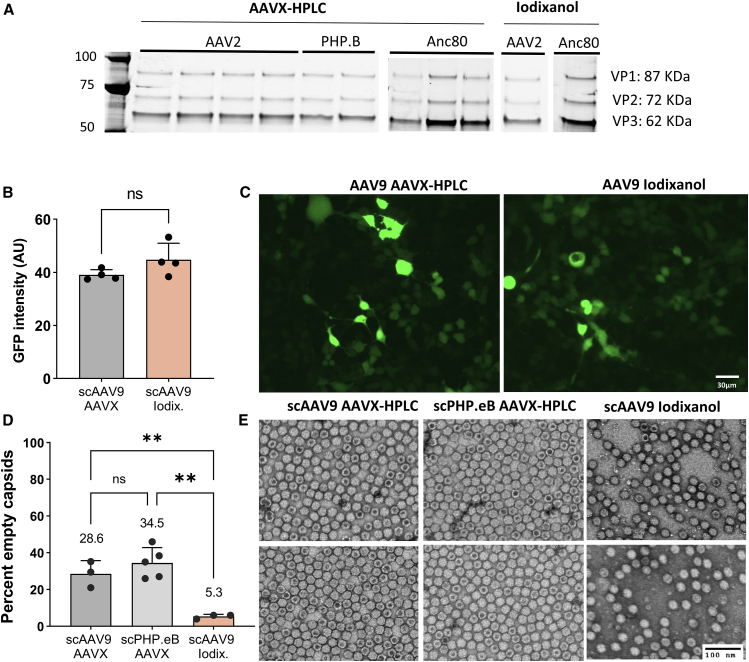
Figure 4.
Quality and in vitro bioactivity of AAVX affinity-purified AAV
(A) SYPRO Ruby-stained protein gel analysis of AAVX-HPLC versus iodixanol ultracentrifugation purified vectors. Most preps show clear, distinct VP1–VP3 bands, with few non-specific bands present, indicating comparable purity with iodixonal purified virus. (B) Quantification empty capsid content using negative stained TEM. Approximately N = 200 particles were counted for each prep from two separate images by two blinded researchers. Statistical significance was assessed using one-way ANOVA with follow-on Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (C) Representative micrographs of AAVX and iodixanol purified preps used to perform the quantification, with two representative images shown for each. (D) In vitro infectivity of AAVX and iodixanol ultracentrifugation purified scAAV9 preps on HEK293 cells. Statistical significance was assessed using two-tailed t test. (E) Representative images used to perform the quantification in (D). ∗∗p < 0.01; ns (not significant), p > 0.05. Error bars denote standard deviation in all panels. See also Figures S5–S7 for full images of SYPRO Ruby gels, GFP micrographs, and TEM micrographs, respectively.