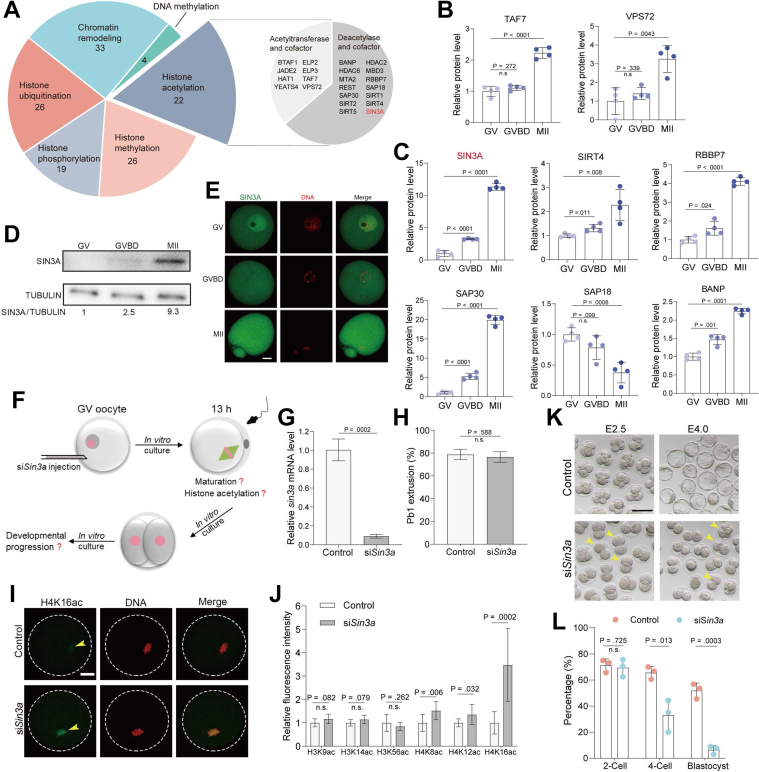
Fig. 4.
SIN3A Regulates Histone Deacetylation in Mouse Oocytes.A, pie plot showing the epigenetic modulators in oocytes. Histone acetylases, deacetylases, and their cofactors are shown in the right pie plot. B, relative abundance of two histone acetyltransferases at GV, GVBD, and MII stages. C, relative abundance of six histone deacetylases in oocytes of GV, GVBD, and MII stages. D, SIN3A protein expression measured by Western blot at GV, GVBD, and MII stages. E, immunostaining analysis of SIN3A distribution in GV, GVBD, and MII oocytes. DNA was stained with propidium iodide. The scale bar represents 20 μm. F, schematic presentation of the experimental design to investigate the role of SIN3A during oocyte development. G, the efficiency of Sin3a siRNA knockdown was determined by RT-qPCR. H, rate of Pb1 extrusion in control oocytes and siSin3a oocytes. I, representative images of H4K16ac fluorescence in control oocytes and siSin3a oocytes. The scale bar represents 20 μm. J, quantitative analysis of fluorescence intensity of acetylated histones. K, bright-field images of E2.5 embryos and E4.0 embryos derived from control and siSin3a oocytes. The scale bar represents 100 μm. L, percentage analysis of development rate in two-cell embryos, four-cell embryos, and blastocysts derived from control and siSin3a oocytes. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD from three independent experiments in which at least 100 oocytes were analyzed for each group. For statistical analysis, a two-tailed Student’s t test was used in all panels, compared with GV or control. n.s., not significant.