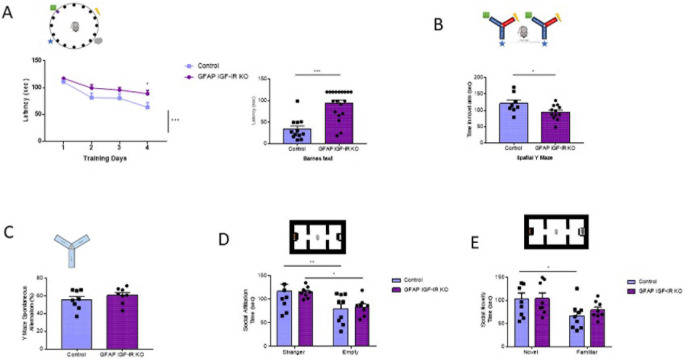
Figure 3. Cognitive traits in mice lacking IGF-I receptors (IGF-IR) in GFAP astrocytes (GFAP-IGF-IR KO mice).
A, Spatial learning in the Barnes maze (upper drawing) was markedly affected in GFAP IGF-IR KO mice, showing significantly reduced memory (control n= 12, GFAP IR KO n=19, training days: 2-way ANOVA, time factor, F(3,122)=12.7; ***p<0.001, Sidak's multiple comparisons test, control vs GFAP 4 th day of training, *p<0.05; test day: Mann-Whitney U: 21.5, ***p<0.001). B, Time spent in the novel arm of the Y maze (upper drawing), a measure of spatial memory, was reduced in GFAP IGF-IR KO mice (control n= 8, GFAP IGF-IR KO n=12, t-test, t= 2.26, *p<0.05). C, Number of spontaneous alternations in a Y maze, a measure of working memory (upper drawing), was similarly unaltered in adult GFAP IGF-IR KO mice (n=8 per group; t-test; t=0.98, p=0.342). D, Social affiliation, as determined by time spent with a stranger mouse vs an empty cage (upper drawing), was normal in GFAP IGF-IR KO mice (control n=9, GFAP IGF-IR KO n=8, 2-way RM ANOVA, condition factor, F(1,15)=19.13; ***p<0.001, Sidak's multiple comparisons test, control familiar mice vs empty cage, **p<0.01, GFAP IR KO familiar vs empty cage, *p<0.05). E, Social novelty, as measured by time spent with a novel partner (upper drawing), was impaired in GFAP IGF-IR KO mice (control n=9, GFAP IGF-IR KO n=8, 2-way RM ANOVA, condition factor, F(1,15)=11.18; **p<0.01, Sidak's multiple comparisons test, control novel mice vs familiar mice, *p<0.05, GFAP IGF-IR KO novel mice vs familiar mice, p=0.16). GFAP=glial fibrillary astrocytic protein.