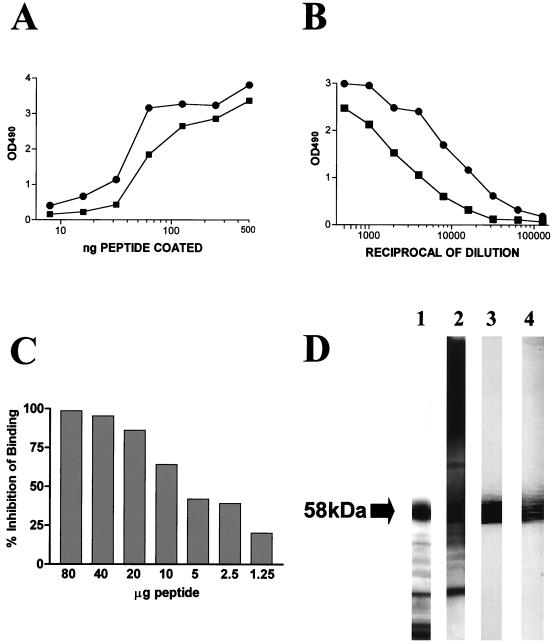
FIG. 6.
Characterization of the two antisera generated in mice against the KLH-conjugated synthetic peptide encompassing the 10 amino acid residues (HTHADGEVHC) at the C terminus of C. albicans mp58. (A) Results of an experiment in which the wells of a microtiter plate were coated with decreasing amounts of free (unconjugated) decapeptide and incubated with a 1:1,000 dilution of anti-peptide antisera (dose-response ELISA). (B) Titration curves of the resulting antisera (endpoint ELISA), for which wells of a microtiter plate were coated with a fixed amount of 1 μg of free peptide per well. (C) Results of a competitive-inhibition ELISA in which different quantities of free soluble decapeptide inhibited binding of the anti-peptide antiserum to solid-phase-coated peptide in a dose-dependent manner. Binding of the uninhibited antibody was considered 100% (0% inhibition). The values shown represent the results from a single experiment. The experiment was repeated with similar results. (D) Results of an immunoblot experiment where the anti-peptide antisera (lanes 3 and 4) were able to recognize mp58 with high specificity among other cell wall components present in the nitrocellulose membrane as revealed by Coomassie staining (lane 1) and immunoblot analysis with rabbit polyclonal antiserum generated against cell wall extracts of the fungus (lane 2). OD490, optical density at 490 nm.