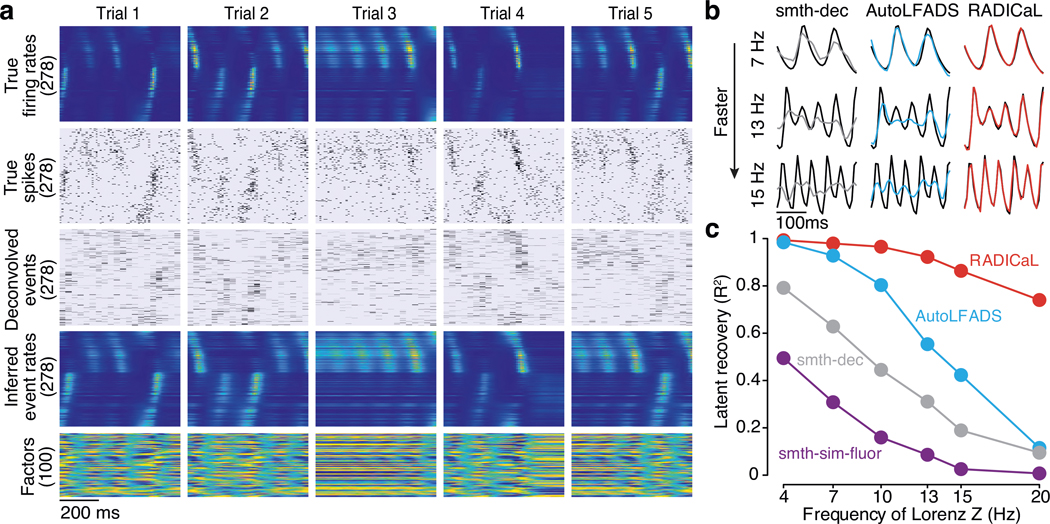
Figure 2 |. Application of RADICaL to synthetic data.
(a) Example firing rates and spiking activity from a Lorenz system simulated at 7 Hz, deconvolved calcium events (inputs to RADICaL), and the corresponding rates and factors inferred by RADICaL. Simulation parameters were tuned so that the performance in inferring spikes using OASIS matched previous benchmarks13 (see Methods). (b) True and inferred Lorenz latent states (Z dimension) for a single example trial from Lorenz systems simulated at three different Lorenz oscillation frequencies. Black: true. Colored: inferred. (c) Performance in estimating the Lorenz Z dimension as a function of simulation frequency was quantified by variance explained (R2) for all 4 methods.