Figure 1.
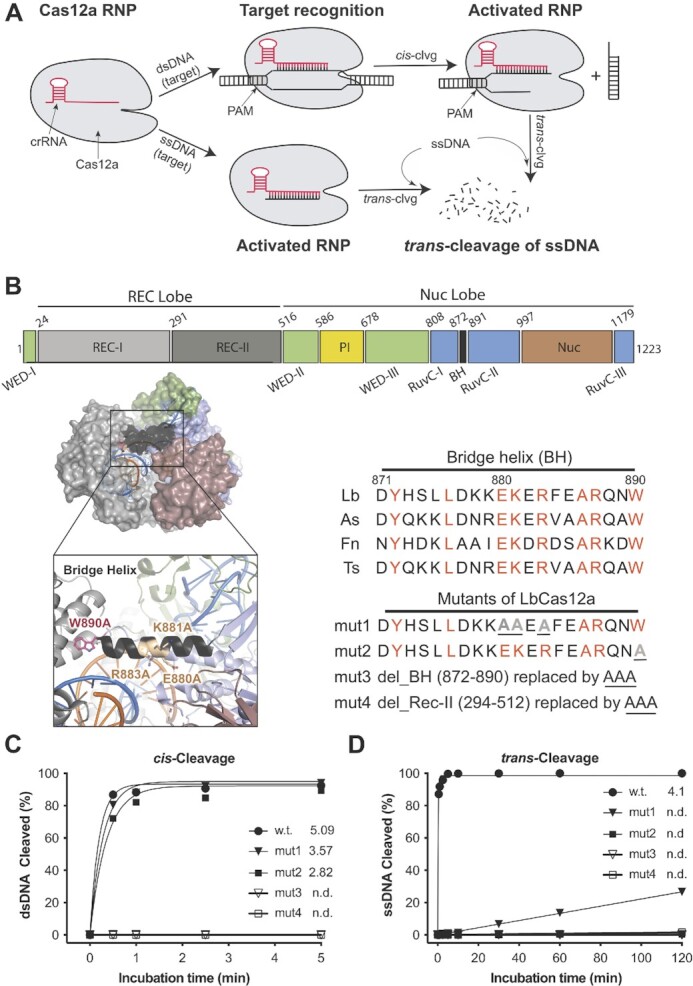
Importance of the bridge helix (BH) of LbCas12a protein in regulating its nuclease activities. (A) Illustration of cis- and trans-cleavage activities of Cas12a proteins. Trans-activity of Cas12a RNP can be activated by either direct binding to target ssDNA or after processing its target dsDNA. (B) Schematic presentation of LbCas12a protein. Domain assignment for LbCas12a (upper panel), protein structure (PDB ID: 5XUS) highlighting the bridge helix in LbCas12a (lower panel, left), and bridge helix sequences of different Cas12a orthologs and designed mutations from LbCas12a (lower panel, right). Point mutations are underlined, and deletions are replaced with a triple alanine sequence (AAA) which is also underlined. (C) and (D). In vitro kinetic studies of cis- and trans-cleavage activities by the wild-type (WT) protein and four designed mutants, mut1-4. Each data point is averaged from two independent assays. In the cis-cleavage assays, the non-target strand (NTS) of the dsDNA substrate was 5’-end-labeled with γ-32P-ATP. In the trans-cleavage assays, a ssDNA substrate was 5’-end-labeled with γ-32P-ATP. Initial reaction rates are given after each protein symbol; n.d., not detected.
