Figure 4.
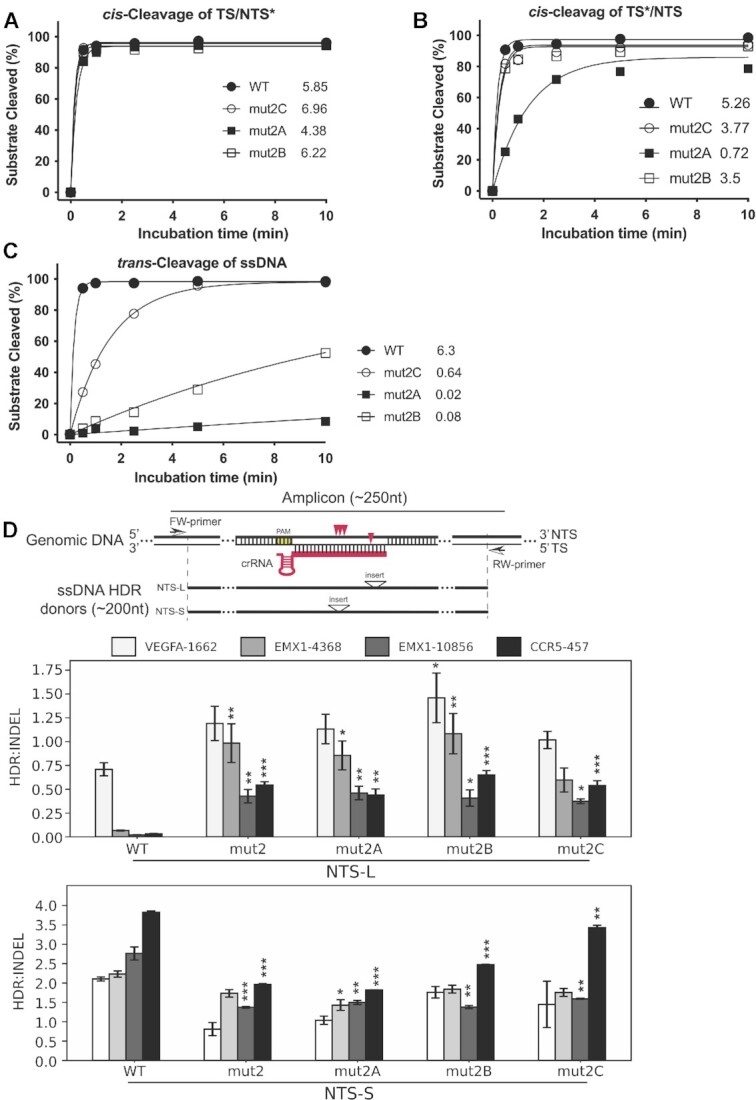
Enhanced activity of mut2A-C in vitro and in cells. (A–C) In vitro kinetic studies of the cleavage activities on NTS (A) and TS (B) in a dsDNA as well as the trans-cleavage activities (C). * indicates labeled strand. In these in vitro kinetic studies, the labeled strand was fluorescently labeled at the 5’-end with FAM. Each data point is averaged from three independent assays. All three beneficial mutants from directed evolution are more active than mut2. mut2B and mut2C display similar cis-activities on both strands as wild-type, but their trans-activities are dramatically lower relative to the wild-type. (D) Genome editing activity of mut2A-C in HEK293 cells. The upper panel shows the nontarget strand (NTS) ssDNA donors of NTS-L and NTS-S defined by the location of inserts from PAM. Specifically, the insert in NTS-L is located at 20–24nt from PAM, while the insert in NTS-S is located at 11–14nt from PAM. Red arrowheads indicate cleavage sites of LbCas12 proteins on target genomic DNA. Insert above the triangle means an exogenous restriction site is inserted as code for calculation of the rate of HDR. The length of ssDNA donors used in this study is less than 200nt, and the length of PCR amplicons is less than 250nt. The other two panels show the ratios of HDR:indel calculated from the averaged NGS data from NTS-L (middle panel) and NTS-S (bottom panel). The three beneficial mutants from the selection display much better activities in genome editing in HEK293 cells when donor NTS-L is used. Significance tests were carried out between each mutant and the wild-type protein. Values represent the replicate average ± standard error of the mean, where n = 2 for NTS-S experiments. For NTS-L experiments, n = 3 for EMX1-10856 and CCR5-457 and n = 4 for EMX1-4368 and VEGFA-1662. P-values were determined using two-sided Dunnett's test: * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001.
