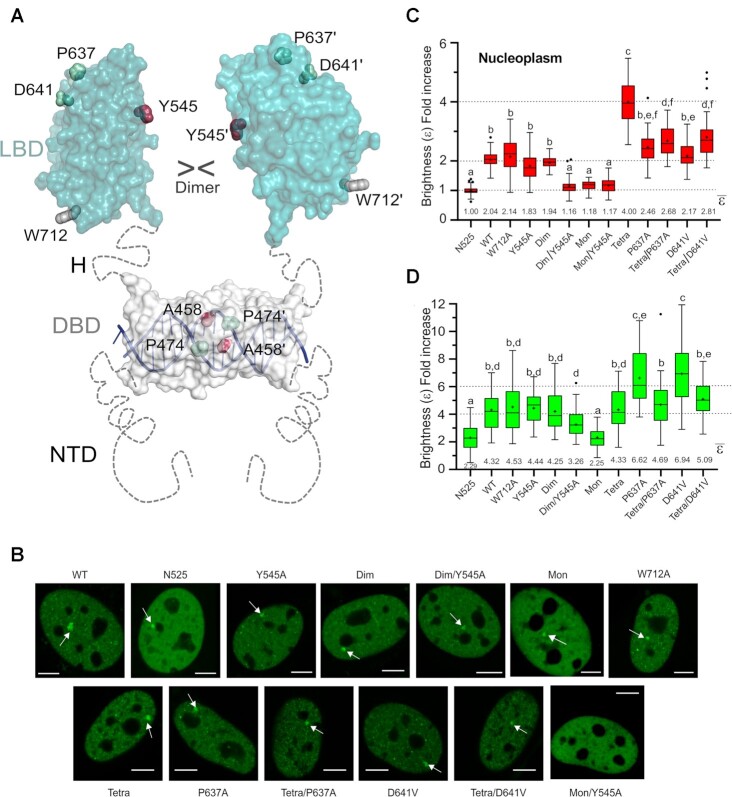
Figure 6.
Mutation of LBD–LBD interface residues profoundly affects the multimerization behavior of FL-GR. (A) Schematic 3D model of FL-GR. The NTD is highly disordered and is followed by the globular DBD (DNA-bound conformation is shown) and the LBD. Note that the length and flexibility of the hinge (H) allows for the formation of various homodimers. The side chains of all residues mutated to assess the multimerization behavior of GR are shown as spheres. (B) Subcellular localization of WT GFP-mGR and indicated mutants in 3617-GRKO cells, as assessed by fluorescence microscopy. Variant N525* lacks the entire LBD and remains monomeric, irrespective of DEX treatment (23). White arrowheads point to the MMTV arrays. Scale bar: 5 μm. Data for WT_GR, GRdim, GRmon and GRtetra were taken from (24) and are shown for comparison purposes. All N&B experiments have been performed with mouse GR as in (23). However, residue numbers correspond to the human protein to facilitate comparisons. (C) GR oligomerization in the nucleus, as determined in N&B assays. The fold increase in molecular brightness (ϵ) relative to the N525* monomeric control is shown (N = 428 total cells with 21 < N < 37 between treatments). (D) Quaternary structure of DNA-bound GR. The results of N&B assays at the MMTV arrays are represented as in panel C (N = 338 total cells with 17 < N < 35 between treatments). Note that simultaneous disruption of intermonomer interactions mediated by the DBD (Ala458Thr) and the LBD (Tyr545Ala) in the GRdim/Y545A double mutant results in a variant that is monomeric in the nucleus, while at the array it formed mostly trimers. In panels (C) and (D), centered lines show the medians and crosses represent sample means (average numbers below each box-plot). Box limits indicate the 25th and 75th percentiles; whiskers extend 1.5-fold the interquartile range from the 25th and 75th percentiles, with outliers represented by dots. Boxes with different superscript letters are significantly different from each other (P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test).