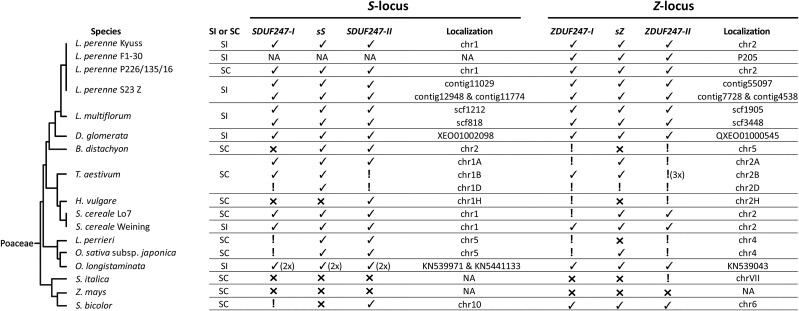
Fig. 6.
Composition of the self-incompatibility candidate genes in 17 genotypes representing 13 different Poaceae species. The phylogenetic tree (left), representing the different species, was drawn according to the NCBI taxonomy database. The compatibility phenotypes are indicated for each genotype: self-incompatible (SI) or self-compatible (SC). A checkmark (✓) represents the presence of a functional gene, and an exclamation mark (! ) indicates that the sequence is present but was evaluated to be non-functional. A cross (x) means no orthologous sequence was found. In addition, the position on chromosome or scaffold level of the self-incompatibility candidate genes in the genome is given. For the Lolium perenne L. genotype S23 Z and Lolium multiflorum Lam., both haplotypes of the diploid assemblies are given. Triticum aestivum L. represents an allohexaploid species leading to a triplication of the S- and Z-locus. Besides, on chromosome 2B (chr2B), a non-functional copy of the ZDUF247-II was present three times. In Oryza longistaminata A. Chev. & Roehr, the gene copies of functional S self-incompatibility candidate genes are present twice on two different scaffolds.