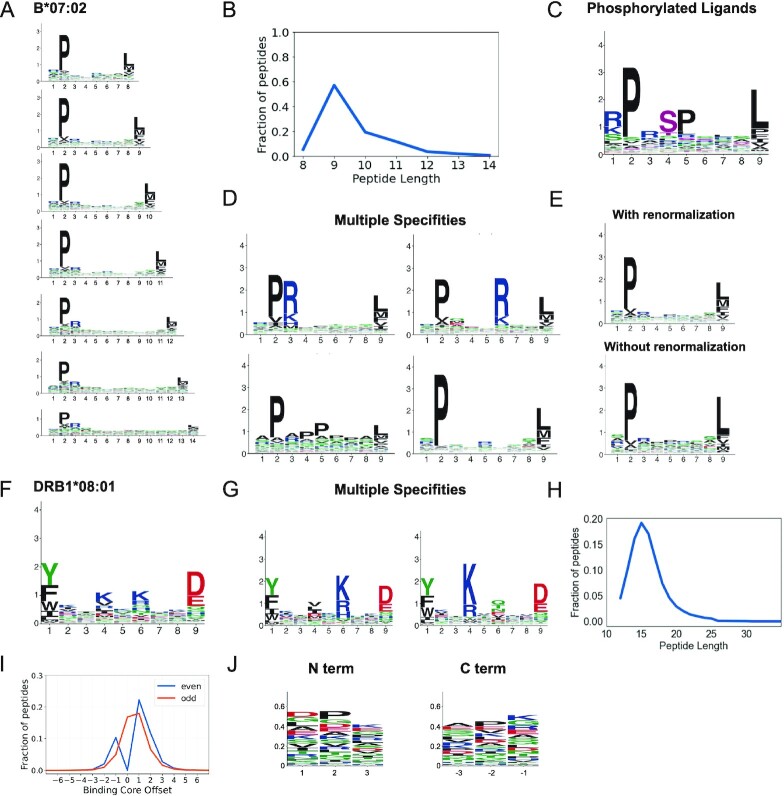
Figure 2.
Binding specificities of MHC molecules. (A) MHC-I binding motifs for different peptide lengths. (B) Peptide length distribution. (C) Motifs for phosphorylated ligands. (D) MHC-I multiple specificities, including mutual exclusivity of charged amino acids at P3 and P6. (E) Illustration of the difference between motifs with and without background frequency renormalization. (F) MHC-II binding motifs. (G) MHC-II multiple specificities capturing a mutual exclusivity of positively charged amino acids at P4 and P6 (see (13)). (H) Average peptide length distribution for MHC-II ligands. (I) Distribution of peptide binding core offsets for MHC-II ligands of even and odd lengths (0 corresponds to a binding core at the middle of peptides with an odd length, and is not defined for peptides with an even length). (J) Motifs in the first and last three N- and C-terminal residues of MHC-II ligands. Panels A–E are built from HLA-B*07:02 ligands. Panels F–G are built from HLA-DRB1*08:01 ligands. Panels H–J are built from all MHC-II ligands (see (13)).