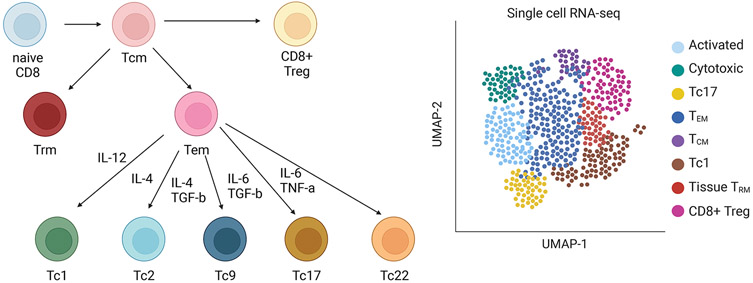
Figure 4. CD8+ subsets and heterogeneity.
CD8+ cells comprise several subsets. These include effector memory CD8+ T cells, which promote early immune responses; long-lived central memory CD8+ cells, which prevent reinfection; and resident memory CD8+ T cells, which reside in mucosal tissues and prevent influx of pathogens. Effector memory T cells are described to have several of their own subgroups, analogous to CD4+ helper subsets. Tc1 are analogous to Th1 and produce IFN-γ, Tc2 are analogous to Th2 and produce type 2 cytokines, Tc9 are analogous to Th9 and produce IL-9, Tc17 are analogous to Th17 and produce IL-17A, and Tc22 are analogous to Th22 and produce IL-22. In vivo, CD8+ T cells are characterized by a large amount of heterogeneity and overlap between these various subsets, with specific clones potentially co-expressing elements of multiple different subsets. This complexity is illustrated by single cell transcriptomic analyses.