Fig. 1.
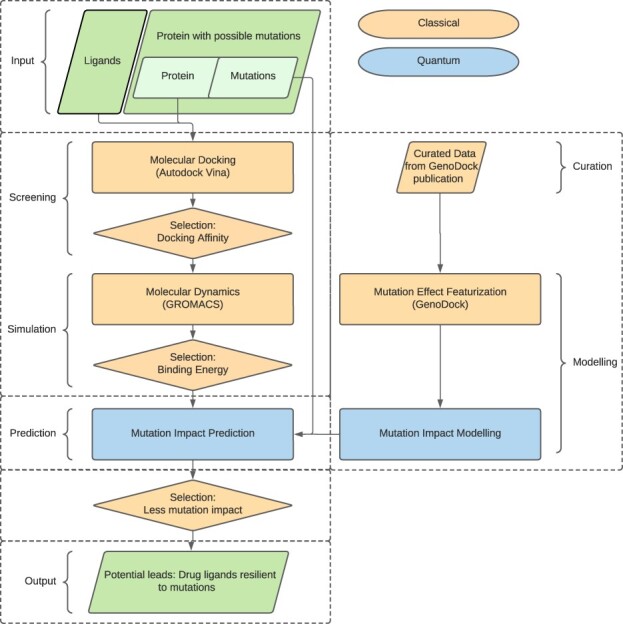
Given a set of ligands and a target protein with known or hypothetical mutations, the classical/quantum hybrid screening pipeline seeks for potential leads—ligands that would bind favorably to the protein as well as its mutants (green parallelograms, representing the input data and output results). The current implementation performs classical computation with down-selection after screening and simulation. Using a set of curated data, featurization is performed before modeling by QML (blue rectangles). The impact of mutations on the down-selected ligands is then by the QML (blue rectangles). Further down-selection based on mutation impact is performed classically. We note that the selection is effectively an optimization or ranking problem, which, along with docking and molecular simulation, could be considered to have a quantum computational approach in the future
