Fig. 2.
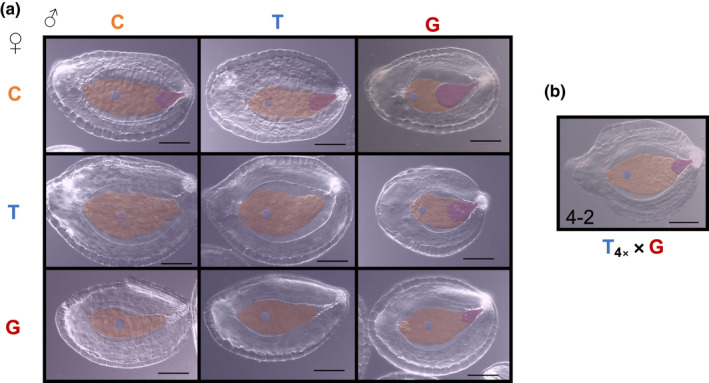
Developing seeds 4 d after pollination (DAP) in crosses among Mimulus caespitosa (C), Mimulus tilingii (T), and Mimulus guttatus (G). Developing seeds were cleared with Hoyer's solution. Structures were outlined and artificially shaded: blue shading represents the embryo, orange shading represents the endosperm region, and purple shading represents the chalazal haustorium. Bars, 0.1 mm. (a) Representative seeds 4 DAP of intra‐ and interspecific crosses. Maternal parent is listed along the left side, and paternal parent is listed along the top. Along the diagonal are the intraspecific crosses (C×C, T×T, and G×G), below the diagonal are maternal‐excess crosses (T×C, G×T, and G×C), and above the diagonal are paternal‐excess crosses (C×T, T×G, and C×G). (b) Representative seed of interploidy cross at 4 DAP. In the bottom left corner, ‘4–2’ indicates that the cross was between two ploidy levels, with the tetraploid maternal parent ploidy listed first. The ‘4x’ subscript in T4x ×G further indicates that the maternal M. tilingii parent is a synthetic tetraploid.
