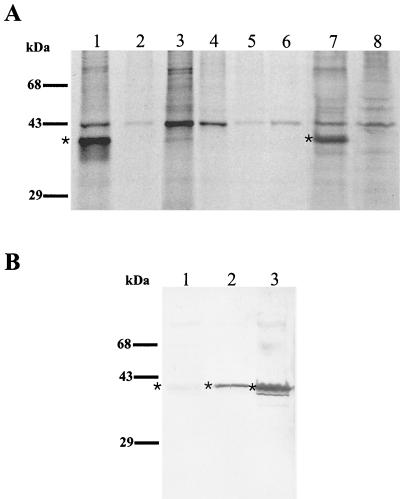
FIG. 4.
(A) Immunoprecipitation of intrinsically 35S-labeled C. pneumoniae antigen by C. pneumoniae MAbs. Autoradiographs show immunoprecipitation results of 35S-labeled C. pneumoniae-infected (lane 1) and uninfected (lane 2) HeLa cells with the GZD1E8 MAb; 35S-labeled C. pneumoniae-infected (lane 3) and uninfected (lane 4) HeLa cells immunoprecipitated with anti-rickettsial MAb 8-13A4A10; 35S-labeled C. psittaci GPIC-infected (lane 5) and C. trachomatis L2-infected (lane 6) HeLa cells immunoprecipitated with MAb GZD1E8; and 35S-labeled C. pneumoniae-infected (lane 7) and uninfected (lane 8) HeLa cells immunoprecipitated with MAb RR-402. ∗, the ∼40-kDa protein in C. pneumoniae-infected HeLa cells detected with MAbs GZD1E8 and RR-402 (lanes 1 and 7). (B) Detection of a ∼40-kDa polypeptide with MAbs GZD1E8 and RR-402 by immunoblotting. The 40-kDa polypeptide was not detected with the RR-402 MAb (lane 1) and was weakly detected with the GZD1E8 MAb (lane 2). A very strong reaction was detected with chlamydial, genus-specific, anti-MOMP antibody (lane 3). ∗, the ∼40-kDa protein.