Figure 3.
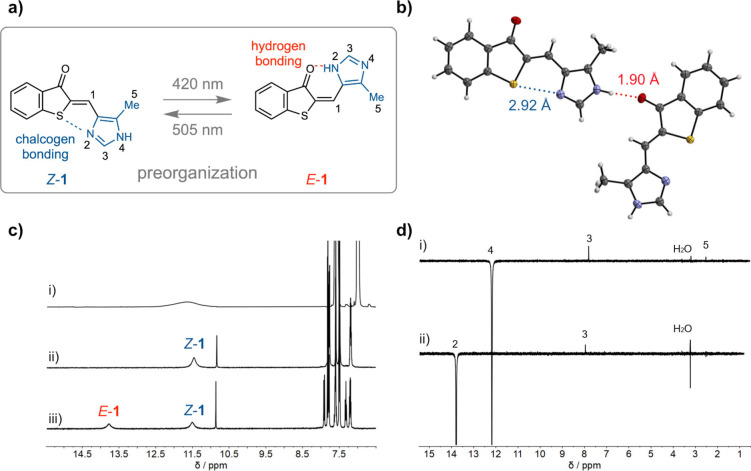
Precise geometry control in Het‐HTI 1. a) Selective chalcogen bonding (blue dotted line) occurs in the Z‐isomer and selective hydrogen bonding (red dotted line) in the E‐isomer. Concomitantly a tautomerization is taking place, which positions the acidic NH proton at different nitrogen atoms of the five membered imidazole ring. b) Evidence of the chalcogen bonding in the crystalline state of Z‐1, intermolecular hydrogen bonding locks the NH proton at N4. c) Evidence of the Z‐1 isomer structure in solution by NMR spectroscopy using chemical shift analysis in THF‐d 8. i) 1H NMR spectrum of imidazole showing the chemical shift of the NH proton as broad signal. ii) 1H NMR spectrum of Z‐1 with a similar shifted NH signal. iii) 1H NMR spectrum of a mixture of Z‐1 and E‐1, for the latter the NH signal is significantly shifted downfield because of intramolecular hydrogen bonding. d) ROE NMR spectra of Z‐1 in THF‐d 8 at −80 °C evidencing the position of the NH proton (signal 4) between protons 3 and 5 and thus the tautomeric and rotameric state of Z‐1.