FIGURE 4.
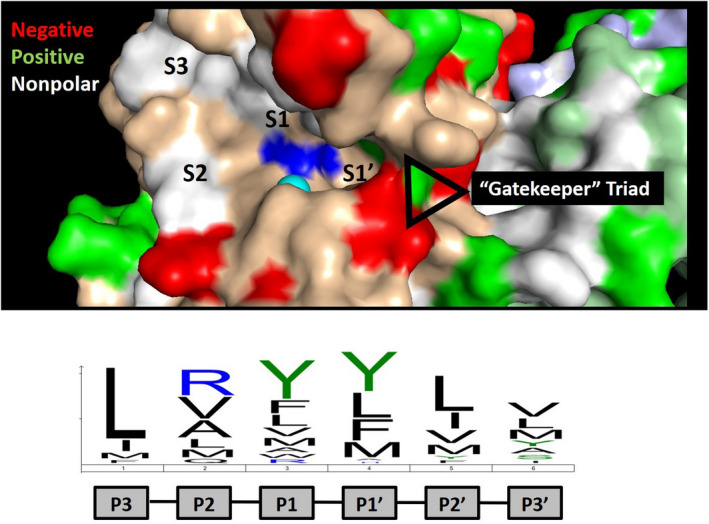
ADAMTS13 active site specificity. The active site of ADAMTS13 is shown with the catalytic zinc (cyan) and glutamic acid (mutated to glutamine; blue) indicated. The active site specificity motif determined by substrate phage display is indicated below, which is dominated by leucine at position P3 and bulky aliphatic amino acids at positions P1 and P1′. 51 These residues are expected to bind to subsites and pockets within the active site, which are indicated. The crystal structure provides evidence of a “gatekeeper” triad at the entrance to the S1′ subsite comprised of Arg193, Asp217, and Asp252 that is predicted to limit access to the active site of ADAMTS13. This ionic interaction is likely overcome by VWF following processive docking to distal exosites, permitting access to the catalytic motif within the active site.
