FIGURE 1.
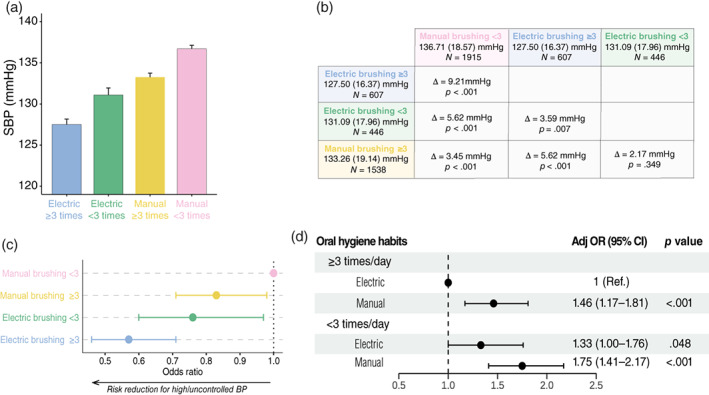
Home oral hygiene habits and blood pressure (BP) profiles. Estimated mean systolic BP (SBP) values based on combinations of brushing frequencies (less or more than three times/day) and modalities (electric or manual toothbrush) (a). Results of multiple pairwise comparisons of mean SBP values across the four strata using Wilcoxon rank test are shown. Bonferroni correction was applied as appropriate (b). Multivariate model (sex, age, BMI, current smoking, diabetes, hypercholesterolaemia, daily vegetable/fruit consumption, and physical activity) indicates that, compared with manual brushing less than three times per day, other combinations of brushing frequency and modality are associated with reduced odds of prevalent/uncontrolled hypertension with various extent (c). Adjusted interaction analysis was performed on the multivariate model using the same process described in Table 3. Forest plot indicates relative adjusted odds ratio (ORs) with 95% confidence interval (CI). Relative excess risk due to interaction: −0.02 (95% CI −0.47 to 0.43); attributable proportion: −0.01 (95% CI −0.25 to 0.23); synergy index: 0.98 (95% CI 0.59–1.61) (d). ***p < .001; **p < .01; *p < .05
