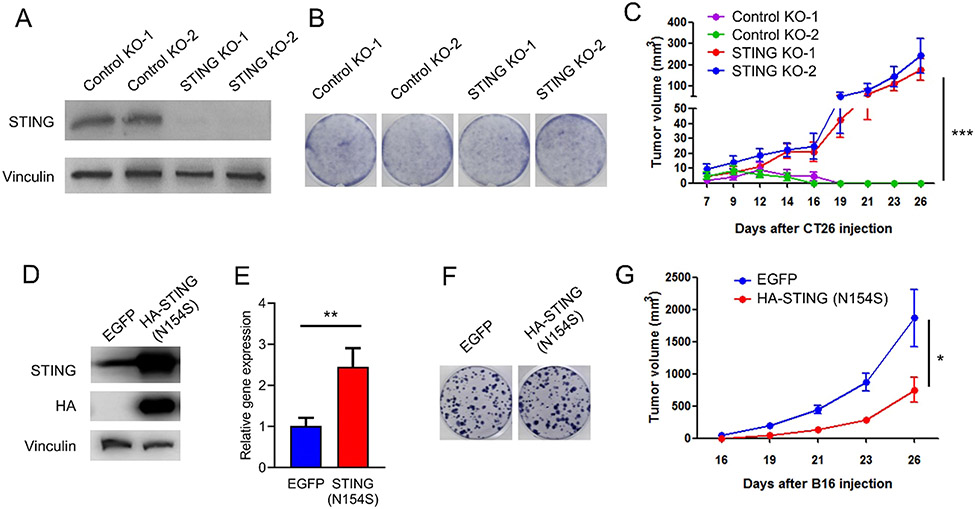
Fig. 3.
STING regulates tumor growth in immunocompetent mice. (A) Western blot analysis of STING expression in two independent control knockout, and two independent STING knockout CT26 cell lines. (B) Colony formation of the controls and STING knockout CT26 cell lines. (C) In vivo tumor growth curves of controls and STING knockout CT26 cell lines. N = 10. (D) Western blot analysis of STING expression in EGFP or STING (N154S)-overexpressed B16F10 cell lines. (E) RT-qPCR analysis of IFNβ expression in EGFP or STING (N154S)-overexpressed B16F10 cell lines. (F) Colony formation of EGFP or STING(N154S) overexpressed B16F10 cells. (G) In vivo tumor growth curves of control and STING (N154S)-overexpressed B16F10 cell lines. N = 6. * P < 0.05, * * P < 0.01, * ** P < 0.001.